Page 241 - Elementary_Linear_Algebra_with_Applications_Anton__9_edition
P. 241
Vector Form of Equation of a Plane
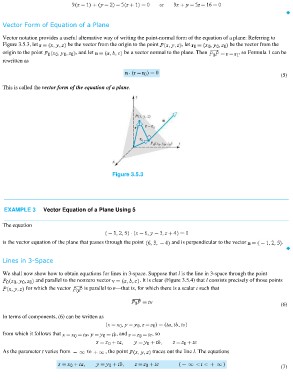
Vector notation provides a useful alternative way of writing the point-normal form of the equation of a plane: Referring to
Figure 3.5.3, let be the vector from the origin to the point , let be the vector from the
origin to the point , and let be a vector normal to the plane. Then , so Formula 1 can be
rewritten as
(5)
This is called the vector form of the equation of a plane.
Figure 3.5.3
EXAMPLE 3 Vector Equation of a Plane Using 5
The equation
is the vector equation of the plane that passes through the point and is perpendicular to the vector .
Lines in 3-Space
We shall now show how to obtain equations for lines in 3-space. Suppose that l is the line in 3-space through the point
and parallel to the nonzero vector . It is clear (Figure 3.5.4) that l consists precisely of those points
for which the vector is parallel to v—that is, for which there is a scalar t such that
(6)
In terms of components, (6) can be written as
from which it follows that , , and , so
As the parameter t varies from to , the point traces out the line l. The equations
(7)