Page 98 - Lecture Notes DCC3113
P. 98
FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT DESIGN
7.1 THE BASIC DESIGN OF FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT
Pavement Thickness Design is the determination of required thickness of various pavement layers to
protect a given soil condition for a given wheel load
Aim: to design a structure that will ensure that the transmitted stresses are sufficiently reduced and do
not exceed the capacity of the underlying subgrade.
7.1.1 The factors that are considered in designing the thickness of flexible pavement.
a. Failure criteria
b. Traffic loading
c. Traffic decaying power
d. Environmental effect
Failure criteria
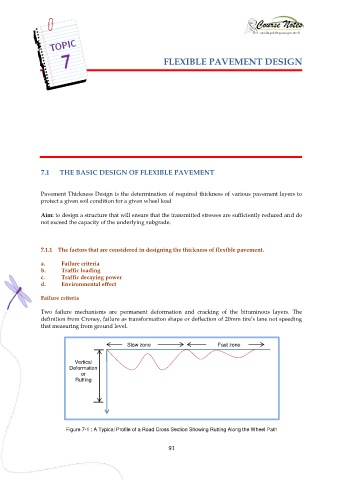
Two failure mechanisms are permanent deformation and cracking of the bituminous layers. The
definition from Croney, failure as transformation shape or deflection of 20mm tire’s lane not speeding
that measuring from ground level.
Slow zone Fast zone
Vertical
Deformation
or
Rutting
Figure 7-1 : A Typical Profile of a Road Cross Section Showing Rutting Along the Wheel Path
91