Page 9 - Livestock Production E Magazine-893
P. 9
INTRADERMAL APPLICATION
OF VACCINES IN PIGS
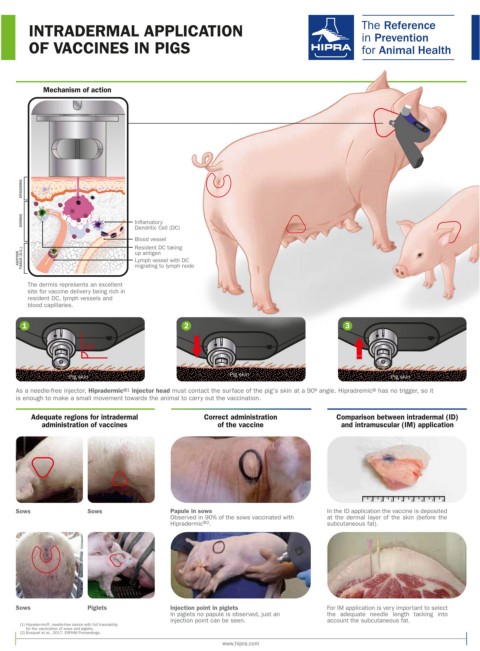
Mechanism of action
EPIDERMIS
DERMIS Inflamatory
Dendritic Cell (DC)
Blood vessel
Resident DC taking
ADIPOSE TISSUE (S.C.) up antigen
Lymph vessel with DC
migrating to lymph node
The dermis represents an excellent
site for vaccine delivery being rich in
resident DC, lymph vessels and
blood capillaries.
1 2 3
90º
Pig skin Pig skin Pig skin
As a needle-free injector, Hipradermic ®1 injector head must contact the surface of the pig's skin at a 90º angle. Hipradremic ® has no trigger, so it
is enough to make a small movement towards the animal to carry out the vaccination.
Adequate regions for intradermal Correct administration Comparison between intradermal (ID)
administration of vaccines of the vaccine and intramuscular (IM) application
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Sows Sows Papule in sows In the ID application the vaccine is deposited
Observed in 90% of the sows vaccinated with at the dermal layer of the skin (before the
®2
Hipradermic . subcutaneous fat).
Sows Piglets Injection point in piglets For IM application is very important to select
In piglets no papule is observed, just an the adequate needle length tacking into
injection point can be seen. account the subcutaneous fat.
(1) Hipradermic ®, needle-free device with full traceability
for the vaccination of sows and piglets.
(2) Busquet et al., 2017. ESPHM Proceedings.
www.hipra.com