Page 255 - Fisika Terapan for Engineers and Scientists
P. 255
Problems 455
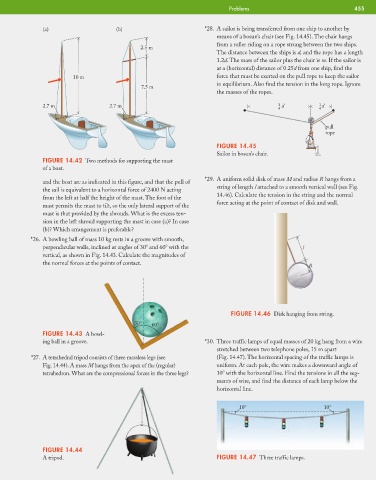
(a) (b) *28. A sailor is being transferred from one ship to another by
means of a bosun’s chair (see Fig. 14.45). The chair hangs
from a roller riding on a rope strung between the two ships.
2.5 m
The distance between the ships is d, and the rope has a length
1.2d. The mass of the sailor plus the chair is m. If the sailor is
at a (horizontal) distance of 0.25d from one ship, find the
10 m force that must be exerted on the pull rope to keep the sailor
in equilibrium. Also find the tension in the long rope. Ignore
7.5 m
the masses of the ropes.
2.7 m 2.7 m 3 d 1 d
4 4
pull
rope
FIGURE 14.45
Sailor in bosun’s chair.
FIGURE 14.42 Two methods for supporting the mast
of a boat.
*29. A uniform solid disk of mass M and radius R hangs from a
and the boat are as indicated in this figure, and that the pull of
string of length l attached to a smooth vertical wall (see Fig.
the sail is equivalent to a horizontal force of 2400 N acting
14.46). Calculate the tension in the string and the normal
from the left at half the height of the mast. The foot of the
force acting at the point of contact of disk and wall.
mast permits the mast to tilt, so the only lateral support of the
mast is that provided by the shrouds. What is the excess ten-
sion in the left shroud supporting the mast in case (a)? In case
(b)? Which arrangement is preferable?
*26. A bowling ball of mass 10 kg rests in a groove with smooth,
perpendicular walls, inclined at angles of 30 and 60 with the l
vertical, as shown in Fig. 14.43. Calculate the magnitudes of
the normal forces at the points of contact.
R
FIGURE 14.46 Disk hanging from string.
30° 60°
FIGURE 14.43 A bowl-
ing ball in a groove. *30. Three traffic lamps of equal masses of 20 kg hang from a wire
stretched between two telephone poles, 15 m apart
*27. A tetrahedral tripod consists of three massless legs (see (Fig. 14.47). The horizontal spacing of the traffic lamps is
Fig. 14.44). A mass M hangs from the apex of the (regular) uniform. At each pole, the wire makes a downward angle of
tetrahedron.What are the compressional forces in the three legs? 10 with the horizontal line. Find the tensions in all the seg-
ments of wire, and find the distance of each lamp below the
horizontal line.
10° 10°
FIGURE 14.44
A tripod. FIGURE 14.47 Three traffic lamps.