Page 7 - Fisika Terapan for Engineers and Scientists
P. 7
7.1 Work 207
SOLUTION: With F 500 N and x 30 m, Eq. (7.1) gives
x
W F x 500 N 30 m 15000 J (7.2)
x
A 1000-kg elevator cage descends 400 m within a skyscraper.
EXAMPLE 2
(a) What is the work done by gravity on the elevator cage during
this displacement? (b) Assuming that the elevator cage descends at constant veloc-
ity, what is the work done by the tension of the suspension cable?
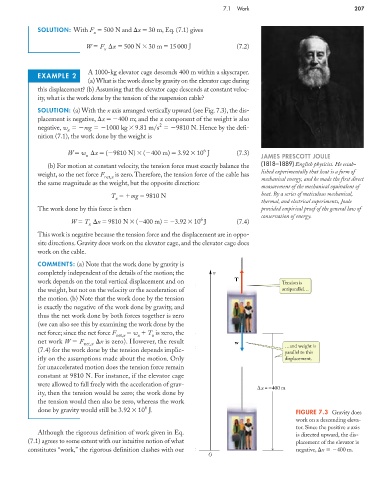
SOLUTION: (a) With the x axis arranged vertically upward (see Fig. 7.3), the dis-
placement is negative, x 400 m; and the x component of the weight is also
2
negative, w mg 1000 kg 9.81 m s 9810 N. Hence by the defi-
x
nition (7.1), the work done by the weight is
6
W w x ( 9810 N) ( 400 m) 3.92 10 J (7.3)
x JAMES PRESCOTT JOULE
(b) For motion at constant velocity, the tension force must exactly balance the (1818–1889) English physicist. He estab-
lished experimentally that heat is a form of
weight, so the net force F is zero.Therefore, the tension force of the cable has
net,x mechanical energy, and he made the first direct
the same magnitude as the weight, but the opposite direction:
measurement of the mechanical equivalent of
T mg 9810 N heat. By a series of meticulous mechanical,
x
thermal, and electrical experiments, Joule
The work done by this force is then provided empirical proof of the general law of
conservation of energy.
6
W T x 9810 N ( 400 m) 3.92 10 J (7.4)
x
This work is negative because the tension force and the displacement are in oppo-
site directions. Gravity does work on the elevator cage, and the elevator cage does
work on the cable.
COMMENTS: (a) Note that the work done by gravity is
completely independent of the details of the motion; the x
work depends on the total vertical displacement and on T Tension is
the weight, but not on the velocity or the acceleration of antiparallel…
the motion. (b) Note that the work done by the tension
is exactly the negative of the work done by gravity, and
thus the net work done by both forces together is zero
(we can also see this by examining the work done by the
net force; since the net force F w T is zero, the
net,x x x
net work W F x is zero). However, the result w
net,x …and weight is
(7.4) for the work done by the tension depends implic- parallel to this
itly on the assumptions made about the motion. Only displacement.
for unaccelerated motion does the tension force remain
constant at 9810 N. For instance, if the elevator cage
were allowed to fall freely with the acceleration of grav-
x = –400 m
ity, then the tension would be zero; the work done by
the tension would then also be zero, whereas the work
6
done by gravity would still be 3.92 10 J. FIGURE 7.3 Gravity does
work on a descending eleva-
tor. Since the positive x axis
Although the rigorous definition of work given in Eq. is directed upward, the dis-
(7.1) agrees to some extent with our intuitive notion of what placement of the elevator is
constitutes “work,” the rigorous definition clashes with our negative, x 400 m.
O