Page 220 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 220
196 Cardio Diabetes Medicine 2017
our recent studies assessing the clinical, biochemical
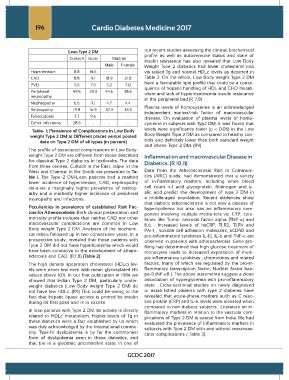
Lean Type 2 DM
profile as well as autoimmune status and state of
Cuttack Jaipur Madras
insulin resistance has also revealed that Low Body
Male Female Weight Type 2 diabetics had lower cholesterol visa
Hypertension 8.8 14.5 - - vis raised Tg and normal HDLc levels as depicted in
CAD 8.8 9.1 18.9 21.0 Table 2. On the whole, Low Body weight Type 2 DM
have a favourable lipid profile that could be a conse-
PVD 5.5 7.5 5.2 7.0
quence of hepatic handling of HDL and CHO metab-
Peripheral 49.5 23.3 44.6 38.6 olism and lack of hyperinsulinemia-insulin resistance
neuropathy
in the peripheral bed.(R 7,8)
Nephropathy 6.6 9.1 4.7 4.4
Plasma levels of homocysteine is an acknowledged
Retinopathy 19.8 16.9 37.3 33.3
independent marker/risk factor of macrovascular
Tuberculosis 7.7 9.6 - - disease. On evaluation of plasma levels of homo-
Other infections 28.6 - - - cysteine in subjects with Typ2 DM, it was found that
Table- 1: Prevalence of Complications in Low Body levels were significantly lower (p < 0.05) in the Low
weight Type 2 DM at Different places versus pooled Body Weight Type 2 DM as compared to healthy con-
data on Type 2 DM of all types (in percent) trols and definitely lower than both standard weight
and obese Type 2 DM. (R9)
The profile of associated complications in Low Body-
weight Type 2 DM are different from those described Inflammation and macrovascular Disease in
for classical Type 2 diabetics in textbooks. The data Diabetics. (R 10,11)
from three centres, Cuttack in the East, Jaipur in the
West and Chennai in the South are presented in Ta- Data from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communi-
ble 1. The Type 2 DM-Lean patients had a marked ties (ARIC) study, had demonstrated that a variety
lower incidence of hypertension, CAD, nephropathy of in-flammatory markers, including white blood
vis-a-vis a marginally higher prevalence of retinop- cell count α-1 acid glycoprotein, fibrinogen and si-
athy and a markedly higher incidence of peripheral alic acid predict the development of type 2 DM in
neuropathy and infections. a middle-aged population. Recent evidences show
that diabetic atherosclerosis is not only a disease of
Peculiarities in prevalence of established Risk Fac- hyperlipidemia but also has an inflammatory com-
tors for Atheroscelosis :Both clinical presentation and ponent involving multiple media-tors viz. CRP, cyto-
mortality profile indicate that neither CAD nor other kines like Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and
macrovascular complications are common in Low IL6. . Increased levels of hsCRP, TLR2, TLR4 and
Body weight Type 2 DM. Analyses of the biochemi- PAI-1 , soluble cell adhesion molecules, sCD40 and
cal milieu followed up in two consecutive years, in a pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α are
prospective study, revealed that those patients with observed in patients with atherosclerosis. Gene pro-
Type 2 DM did not have hyperlipidemia which would filing has determined that high glucose treatment of
have been conducive to the development of athero- monocytes leads to increased expression of multi-
sclerosis and CAD. (R7,8) (Table 2) ple inflammatory cytokines , chemokines and related
The high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDLc) lev- factors, many of which are regulated by the pro-in-
els were never low even with mean glycosylated Hb flammatory transcription factor, Nuclear factor kap-
values above 10%. In our first publication in 1984 we pa-B (NF-κB ). The above statements suggest a close
showed that Indian Type 2 DM, particularly under- association of hyperglycemia with pro-inflammatory
weight diabetics (Low Body weight Type 2 DM) do state . Cross-sectional studies on newly diagnosed
not have low HDLc .(R9) This could be owing to the or estab-lished patients with type 2 diabetes have
fact that hepatic lipase activity is primed by insulin revealed that acute-phase markers such as C reac-
during its first pass and is in excess tive protein (CRP) and IL-6 levels were elevated when
compared to non-diabetic subjects . Literature on in-
in lean patients with Type 2 DM. Its activity is directly flammatory markers in relation to the vascular com-
related to HDLc metabolism. Higher levels of Tg in plications of Type 2 DM is sparse from India. We had
these diabetics were a fact established by us which evaluated the prevalence of inflammatory markers in
was duly acknowledged by the international commu- subjects with Type 2 DM with and without macrovas-
nity. Type-IV dyslipidemia is by far the commonest cular complications ( Table 3).
form of dyslipidemia seen in these diabetics, and
that too in a glycemic uncontrolled state. In one of
GCDC 2017