Page 248 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 248
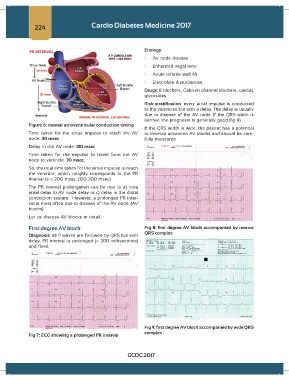
224 Cardio Diabetes Medicine 2017
Etiology:
• AV node disease
• Enhanced vagal tone
• Acute inferior wall MI
• Electrolyte disturbances
Drugs: ß blockers, Calcium channel blockers, cardiac
glycosides
Risk stratification: every atrial impulse is conducted
to the ventricles but with a delay. The delay is usually
due to disease of the AV node. If the QRS width is
narrow, the prognosis is generally good.(fig 8)
Figure 6: normal atrioventricular conduction timing
If the QRS width is wide, the patient has a potential
Time taken for the sinus impulse to reach the AV to develop advanced AV blocks and should be care-
node: 30 msec fully monitored.
Delay in the AV node: 130 msec
Time taken for the impulse to travel from the AV
node to ventricle: 30 msec.
So, the total time taken for the sinus impulse to reach
the ventricle, which roughly corresponds to the PR
interval is < 200 msec. (120-200 msec)
The PR interval prolongation can be due to a) intra
atrial delay b) AV node delay or c) delay in the distal
conduction system. However, a prolonged PR inter-
val is most often due to disease of the AV node. (AV
blocks)
Let us discuss AV blocks in detail.
First degree AV block Fig 8: first degree AV block accompanied by narrow
Diagnosis: all P waves are followed by QRS but with QRS complex
delay. PR interval is prolonged (> 200 milliseconds)
and fixed.
Fig 9: first degree AV block accompanied by wide QRS
complex
Fig 7: ECG showing a prolonged PR interval
GCDC 2017