Page 246 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 246
222 Cardio Diabetes Medicine 2017
Bradyarrhythmias
Dr. Kader Sahib
Consultant. Cardiologist, Trichy.
Definition:
It is important to know what defines a normal sinus
rhythm before we discuss bradyarrhythmia.
Criteria for normal sinus rhythm:
1. P wave upright in Lead 1
2. P wave inverted in avR
3. Constant P-P cycles : that is the next P wave
should come in the next expected time
4. Constant P-R intervals
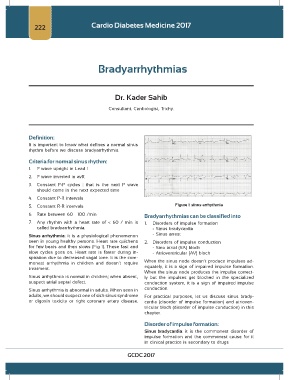
5. Constant R-R intervals Figure 1: sinus arrhythmia
6. Rate between 60 – 100 /min Bradyarrhythmias can be classified into
7. Any rhythm with a heart rate of < 60 / min is 1. Disorders of impulse formation
called bradyarrhythmia. - Sinus bradycardia
Sinus arrhythmia: it is a physiological phenomenon - Sinus arrest
seen in young healthy persons. Heart rate quickens 2. Disorders of impulse conduction
for few beats and then slows (Fig 1). These fast and - Sino atrial (SA) block
slow cycles goes on. Heart rate is faster during in- - Atrioventricular (AV) block
spiration due to decreased vagal tone. It is the com-
monest arrhythmia in children and doesn’t require When the sinus node doesn’t produce impulses ad-
treatment. equately, it is a sign of impaired impulse formation.
When the sinus node produces the impulse correct-
Sinus arrhythmia is normal in children; when absent, ly but the impulses get blocked in the specialized
suspect atrial septal defect. conduction system, it is a sign of impaired impulse
Sinus arrhythmia is abnormal in adults. When seen in conduction.
adults, we should suspect one of sick sinus syndrome For practical purposes, let us discuss sinus brady-
or digoxin toxicity or right coronary artery disease. cardia (disorder of impulse formation) and atrioven-
tricular block (disorder of impulse conduction) in this
chapter.
Disorder of impulse formation:
Sinus bradycardia: it is the commonest disorder of
impulse formation and the commonest cause for it
in clinical practice is secondary to drugs
GCDC 2017