Page 423 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 423
Percutaneous Heart Repair - 399
Can We Replace Open Heart Surgery
curred during the first 6 months. Between 6 months recently.
and 5 years, however, there was no difference be-
tween the percutaneous and surgical groups in the
incidence of surgery for mitral dysfunction. Surgery
was more effective than MitraClip in terms of free-
dom from MR and repeat mitral surgery. MitraClip is
not a replacement for surgery, but rather is a viable
option for selected patients who are thought to be at
prohibitive surgical risk.
A propensity-matched comparison of EVEREST II
HRR/REALISM patients and high-risk Duke Echo-
cardiography Laboratory Database patients man-
aged nonsurgically suggested a survival benefit with
MitraClip therapy at 12 months (relative risk, 0.64;
P = .013). Similarly, a propensity-matched cohort of
120 patients with cardiomyopathy and functional MR
showed improved rates of hospital readmission and
overall survival when MitraClip therapy was com-
pared to optimal medical therapy.
Mitral Valve Replacement experience remains at an
early stage. There have been important challenges
in the development of this technology, including
the complexity of the mitral valve anatomy involv-
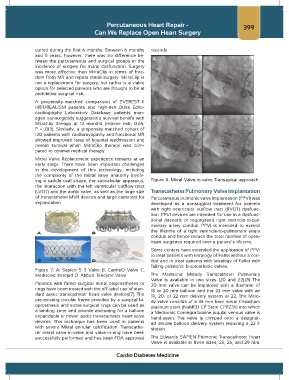
ing a saddle oval shape, the subvalvular apparatus, Figure 8: Mitral Valve-in-valve Transapical approach.
the interaction with the left ventricular outflow tract
(LVOT) and the aortic valve, as well as the large size Transcatheter Pulmonary Valve Implantation
of transcatheter MVR devices and large catheters for Percutaneous pulmonic valve implantation (PPVI) was
implantation. developed as a nonsurgical treatment for patients
with right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) dysfunc-
tion. PPVI devices are intended for use in a dysfunc-
tional (stenotic or regurgitant) right ventricle-to-pul-
monary artery conduit. PPVI is intended to extend
the lifetime of a right ventricle-to-pulmonary artery
conduit and hence reduce the total number of open-
heart surgeries required over a patient’s lifetime.
Some centers have extended the application of PPVI
to treat patients with tetralogy of Fallot without a con-
duit and to treat patients with tetralogy of Fallot with
failing pulmonic bioprosthetic valves.
Figure 7: A: Sapien S 3 Valve B. CardiaQ Valve C.
Medtronic Intrepid D. Abbott Tendyne Valve The Medtronic Melody Transcatheter Pulmonary
Valve is available in two sizes (20 and 22).(8) The
Patients with failed surgical mitral bioprostheses or 20 mm valve can be implanted with a diameter of
rings have been treated with the off-label use of stan- 18 or 20 mm balloon and the 22 mm valve with an
dard aortic transcatheter heart valve devices(7). The 18, 20, or 22 mm delivery system or 22. The Melo-
pre-existing circular frame provided by a surgical bi- dy valve consists of a 34 mm bare metal Cheatham
oprosthesis and some surgical rings can be used as platinum stent (NuMED CP Stent CP8Z34) into which
a landing zone and provide anchoring for a balloon a Medtronic Contegra bovine jugular venous valve is
expandable or newer aortic transcatheter heart valve hand-sewn. The valve is crimped onto a designat-
devices. This technique has been used in patients ed double balloon delivery system requiring a 22 F
with severe Mitral annular calcification. Transcathe- sheath.
ter mitral valve-in-valve and valve-in-ring have been
successfully performed and has been FDA approved The Edwards SAPIEN Pulmonic Transcatheter Heart
Valve is available in three sizes, 23, 26, and 29 mm.
Cardio Diabetes Medicine