Page 525 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 525
Cardio Diabetes Medicine 2017 501
efit.Bruno et al reported worse neurological outcome diabetes insipidus, and long-term rehabilitation.
at three months in ischemic stroke patients admitted Intensive Insulin therapy in critically ill patient –The
with higher blood glucose level.
Leuven MICU Study:
In general surgery patients, the relative risk for se- The results of SICU trial prompted this obvious ques-
rious post-operative infections (sepsis, pneumo- tion: would implementation of the same protocol also
nia, and wound infection) increased 5.7 fold when improve outcome for medical ICU patients?
any post-operative day 1 blood glucose (BG) was >
220mg/dL . The authors randomized 1200 medical ICU patients
to strict normalization of blood glucose levels (80 to
Tumul Chowdhury General intensive care 110 mg/dL) with the use of insulin infusion or to con-
for patients with traumatic brain injury: An ventional therapy with a more liberal blood glucose
target (180-200 mg/dL).Surprisingly there was no
update mortality benefit for IIT and there was a significantly
Hyperglycemia Linked to Morbidity: greater occurrence of hypoglycemia in the IIT group
(18.7% vs. 3.1%, p<0.001).In the subgroup of patients
After an ischemic stroke, the degree of hyperglyce- who were in the ICU for fewer than three days, on IIT
mia appears to independently predict infarct expan- appeared to result in a higher mortality rate (26.8%
sion and neurologic outcome.Stress hyperglycemia vs. 18.8%).
also is associated with increased risk for critical
illness polyneuropathy due to cytokine release. Pa-
tients with Critical Illness Polyneuropathy also were
found to have prolonged mechanical ventilation time
and longer ICU stays.
Sub analysis of the Leuven 1 study population, pa-
tients with isolated brain injury were investigated for
degree of intracranial pressure, incidence of seizures,
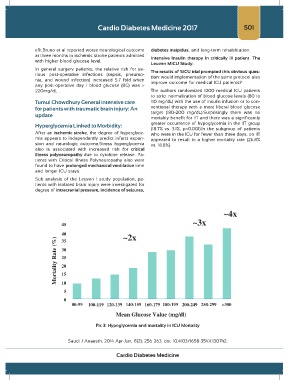
Pic 3: Hypoglycemia and mortality in ICU Mortality
Saudi J Anaesth. 2014 Apr-Jun; 8(2): 256–263. doi: 10.4103/1658-354X.130742.
Cardio Diabetes Medicine