Page 122 - Physics Form 5 KSSM_Neat
P. 122
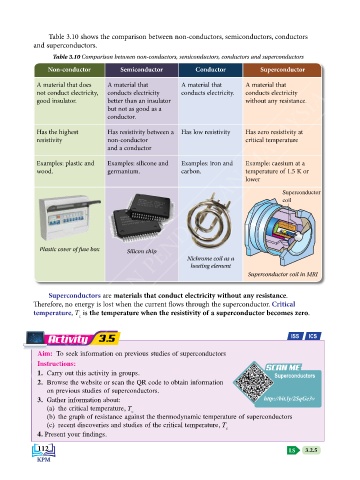
Table 3.10 shows the comparison between non-conductors, semiconductors, conductors
and superconductors.
Table 3.10 Comparison between non-conductors, semiconductors, conductors and superconductors
Non-conductor Semiconductor Conductor Superconductor
A material that does A material that A material that A material that
KEMENTERIAN PENDIDIKAN MALAYSIA
not conduct electricity, conducts electricity conducts electricity. conducts electricity
good insulator. better than an insulator without any resistance.
but not as good as a
conductor.
Has the highest Has resistivity between a Has low resistivity Has zero resistivity at
resistivity non-conductor critical temperature
and a conductor
Examples: plastic and Examples: silicone and Examples: iron and Example: caesium at a
wood. germanium. carbon. temperature of 1.5 K or
lower
Superconductor
coil
Plastic cover of fuse box Silicon chip
Nichrome coil as a
heating element
Superconductor coil in MRI
Superconductors are materials that conduct electricity without any resistance.
Therefore, no energy is lost when the current flows through the superconductor. Critical
temperature, T is the temperature when the resistivity of a superconductor becomes zero.
c
Activity 3.5 ISS ICS
Aim: To seek information on previous studies of superconductors
Instructions: SCAN ME
SCAN ME
1. Carry out this activity in groups. Superconductors
2. Browse the website or scan the QR code to obtain information
on previous studies of superconductors.
3. Gather information about: http://bit.ly/2SqGe3v
(a) the critical temperature, T
c
(b) the graph of resistance against the thermodynamic temperature of superconductors
(c) recent discoveries and studies of the critical temperature, T
c
4. Present your findings.
112 LS 3.2.5