Page 190 - Physics Form 5 KSSM_Neat
P. 190
LET’S ANSWER
Example 1 LET’S ANSWER
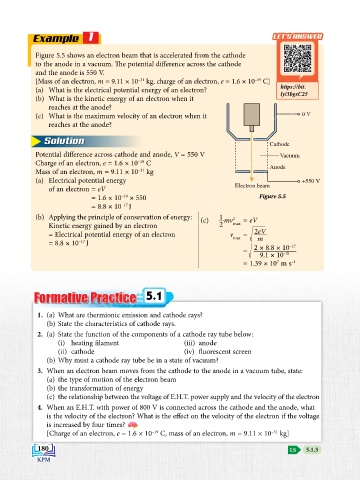
Figure 5.5 shows an electron beam that is accelerated from the cathode
to the anode in a vacuum. The potential difference across the cathode
and the anode is 550 V.
[Mass of an electron, m = 9.11 × 10 kg, charge of an electron, e = 1.6 × 10 C]
–19
–31
(a) What is the electrical potential energy of an electron? https://bit.
(b) What is the kinetic energy of an electron when it ly/3bgsC25
reaches at the anode?
(c) What is the maximum velocity of an electron when it 0 V
reaches at the anode?
Solution Cathode
Potential difference across cathode and anode, V = 550 V Vacuum
Charge of an electron, e = 1.6 × 10 C
–19
Mass of an electron, m = 9.11 × 10 kg Anode
–31
(a) Electrical potential energy +550 V
of an electron = eV Electron beam
= 1.6 × 10 × 550 Figure 5.5
–19
= 8.8 × 10 –17 J
(b) Applying the principle of conservation of energy: (c) 1 mv 2 = eV
Kinetic energy gained by an electron 2 max
2eV
max
v
= Electrical potential energy of an electron
KEMENTERIAN PENDIDIKAN MALAYSIA
=
m
= 8.8 × 10 –17 J –17
= 2 × 8.8 × 10
9.1 × 10
–31
= 1.39 × 10 m s –1
7
Formative Practice 5.1
1. (a) What are thermionic emission and cathode rays?
(b) State the characteristics of cathode rays.
2. (a) State the function of the components of a cathode ray tube below:
(i) heating filament (iii) anode
(ii) cathode (iv) fluorescent screen
(b) Why must a cathode ray tube be in a state of vacuum?
3. When an electron beam moves from the cathode to the anode in a vacuum tube, state:
(a) the type of motion of the electron beam
(b) the transformation of energy
(c) the relationship between the voltage of E.H.T. power supply and the velocity of the electron
4. When an E.H.T. with power of 800 V is connected across the cathode and the anode, what
is the velocity of the electron? What is the effect on the velocity of the electron if the voltage
is increased by four times?
–19
[Charge of an electron, e = 1.6 × 10 C, mass of an electron, m = 9.11 × 10 kg]
–31
180 LS 5.1.3