Page 69 - Physics Form 5 KSSM_Neat
P. 69
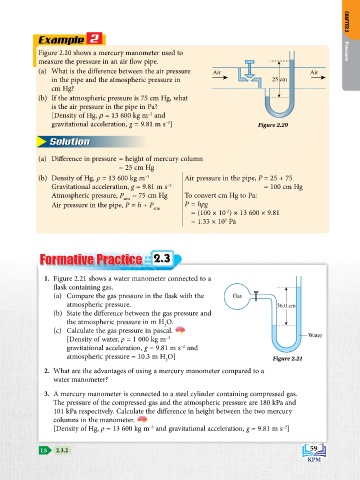
Example 2 CHAPTER 2
Figure 2.20 shows a mercury manometer used to Pressure
measure the pressure in an air flow pipe.
(a) What is the difference between the air pressure Air Air
in the pipe and the atmospheric pressure in 25 cm
cm Hg?
KEMENTERIAN PENDIDIKAN MALAYSIA
(b) If the atmospheric pressure is 75 cm Hg, what
is the air pressure in the pipe in Pa?
–3
[Density of Hg, r = 13 600 kg m and
–2
gravitational acceleration, g = 9.81 m s ] Figure 2.20
Solution
(a) Difference in pressure = height of mercury column
= 25 cm Hg
(b) Density of Hg, ρ = 13 600 kg m –3 Air pressure in the pipe, P = 25 + 75
Gravitational acceleration, g = 9.81 m s –2 = 100 cm Hg
Atmospheric pressure, P = 75 cm Hg To convert cm Hg to Pa:
atm
Air pressure in the pipe, P = h + P P = hρg
atm
= (100 × 10 ) × 13 600 × 9.81
-2
= 1.33 × 10 Pa
5
Formative Practice 2.3
1. Figure 2.21 shows a water manometer connected to a
flask containing gas.
(a) Compare the gas pressure in the flask with the Gas
atmospheric pressure. 36.0 cm
(b) State the difference between the gas pressure and
the atmospheric pressure in m H O.
2
(c) Calculate the gas pressure in pascal.
[Density of water, ρ = 1 000 kg m Water
–3
gravitational acceleration, g = 9.81 m s and
–2
atmospheric pressure = 10.3 m H O] Figure 2.21
2
2. What are the advantages of using a mercury manometer compared to a
water manometer?
3. A mercury manometer is connected to a steel cylinder containing compressed gas.
The pressure of the compressed gas and the atmospheric pressure are 180 kPa and
101 kPa respectively. Calculate the difference in height between the two mercury
columns in the manometer.
[Density of Hg, ρ = 13 600 kg m and gravitational acceleration, g = 9.81 m s ]
–3
–2
LS 2.3.2 59