Page 288 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 288
Chapter 6 CARE OF THE TRAUMATIZED PATIENT 273
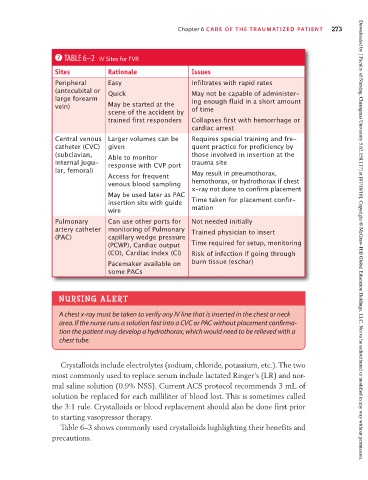
7 TABLE 6–2 IV Sites for FVR
Sites Rationale Issues
Peripheral Easy Infiltrates with rapid rates
(antecubital or Quick May not be capable of administer-
large forearm ing enough fluid in a short amount
vein) May be started at the of time
scene of the accident by
trained first responders Collapses first with hemorrhage or
cardiac arrest
Central venous Larger volumes can be Requires special training and fre-
catheter (CVC) given quent practice for proficiency by
(subclavian, Able to monitor those involved in insertion at the
internal jugu- response with CVP port trauma site
lar, femoral) May result in pneumothorax,
Access for frequent
venous blood sampling hemothorax, or hydrothorax if chest
x-ray not done to confirm placement
May be used later as PAC
insertion site with guide Time taken for placement confir-
wire mation
Pulmonary Can use other ports for Not needed initially
artery catheter monitoring of Pulmonary Trained physician to insert
(PAC) capillary wedge pressure
(PCWP), Cardiac output Time required for setup, monitoring Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
(CO), Cardiac index (CI) Risk of infection if going through
Pacemaker available on burn tissue (eschar)
some PACs
NURSING ALERT
A chest x-ray must be taken to verify any IV line that is inserted in the chest or neck
area. If the nurse runs a solution fast into a CVC or PAC without placement confirma-
tion the patient may develop a hydrothorax, which would need to be relieved with a
chest tube.
Crystalloids include electrolytes (sodium, chloride, potassium, etc.). The two
most commonly used to replace serum include lactated Ringer’s (LR) and nor-
mal saline solution (0.9% NSS). Current ACS protocol recommends 3 mL of
solution be replaced for each milliliter of blood lost. This is sometimes called
the 3:1 rule. Crystalloids or blood replacement should also be done first prior
to starting vasopressor therapy.
Table 6–3 shows commonly used crystalloids highlighting their benefits and
precautions.