Page 289 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 289
274 CRITICAL CARE NURSING DeMYSTIFIED
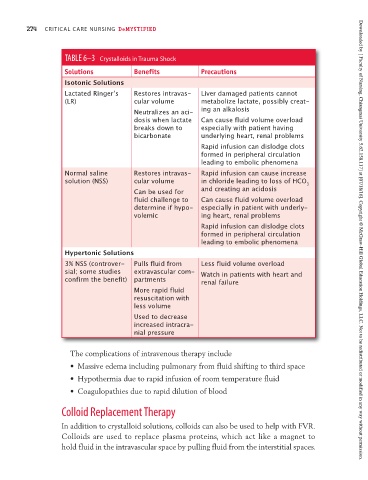
TABLE 6–3 Crystalloids in Trauma Shock
Solutions Benefits Precautions
Isotonic Solutions
Lactated Ringerʼs Restores intravas- Liver damaged patients cannot
(LR) cular volume metabolize lactate, possibly creat-
Neutralizes an aci- ing an alkalosis
dosis when lactate Can cause fluid volume overload
breaks down to especially with patient having
bicarbonate underlying heart, renal problems
Rapid infusion can dislodge clots
formed in peripheral circulation
leading to embolic phenomena
Normal saline Restores intravas- Rapid infusion can cause increase
solution (NSS) cular volume in chloride leading to loss of HCO
3
Can be used for and creating an acidosis
fluid challenge to Can cause fluid volume overload
determine if hypo- especially in patient with underly-
volemic ing heart, renal problems
Rapid infusion can dislodge clots
formed in peripheral circulation
leading to embolic phenomena Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
Hypertonic Solutions
3% NSS (controver- Pulls fluid from Less fluid volume overload
sial; some studies extravascular com- Watch in patients with heart and
confirm the benefit) partments renal failure
More rapid fluid
resuscitation with
less volume
Used to decrease
increased intracra-
nial pressure
The complications of intravenous therapy include
• Massive edema including pulmonary from fluid shifting to third space
• Hypothermia due to rapid infusion of room temperature fluid
• Coagulopathies due to rapid dilution of blood
Colloid Replacement Therapy
In addition to crystalloid solutions, colloids can also be used to help with FVR.
Colloids are used to replace plasma proteins, which act like a magnet to
hold fluid in the intravascular space by pulling fluid from the interstitial spaces.