Page 380 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 380
Chapter 8 CARE OF THE PATIENT WITH CRITICAL RENAL NEEDS 365
abscesses or inflammation. Renal artery stenosis can lead to prerenal failure and
hypertension, which can lead to heart failure. The nursing care pre and post care
is similar to a cardiac catheterization (see Chapter 3 for nursing care).
Medications Commonly Used in Critical Care
3 Medications that affect the renal system include a variety of complex types.
These medications include diuretics, medications to control the unwanted
effects of electrolytes that accumulate when the kidneys fail to function, and
miscellaneous medications (see Table 8–1 to 8–3).
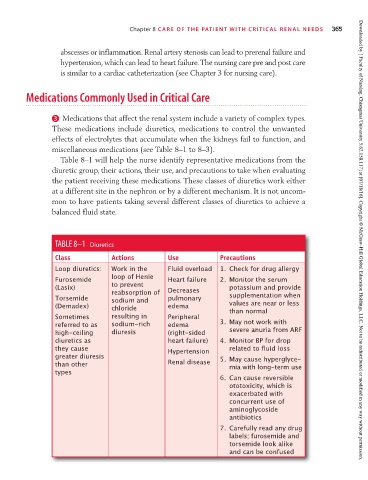
Table 8–1 will help the nurse identify representative medications from the
diuretic group, their actions, their use, and precautions to take when evaluating
the patient receiving these medications. These classes of diuretics work either
at a different site in the nephron or by a different mechanism. It is not uncom-
mon to have patients taking several different classes of diuretics to achieve a
balanced fluid state.
TABLE 8–1 Diuretics Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
Class Actions Use Precautions
Loop diuretics: Work in the Fluid overload 1. Check for drug allergy
Furosemide loop of Henle Heart failure 2. Monitor the serum
(Lasix) to prevent potassium and provide
reabsorption of Decreases
Torsemide sodium and pulmonary supplementation when
(Demadex) chloride edema values are near or less
than normal
Sometimes resulting in Peripheral
referred to as sodium-rich edema 3. May not work with
high-ceiling diuresis (right-sided severe anuria from ARF
diuretics as heart failure) 4. Monitor BP for drop
they cause Hypertension related to fluid loss
greater diuresis 5. May cause hyperglyce-
than other Renal disease mia with long-term use
types
6. Can cause reversible
ototoxicity, which is
exacerbated with
concurrent use of
aminoglycoside
antibiotics
7. Carefully read any drug
labels; furosemide and
torsemide look alike
and can be confused