Page 384 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 384
Chapter 8 CARE OF THE PATIENT WITH CRITICAL RENAL NEEDS 369
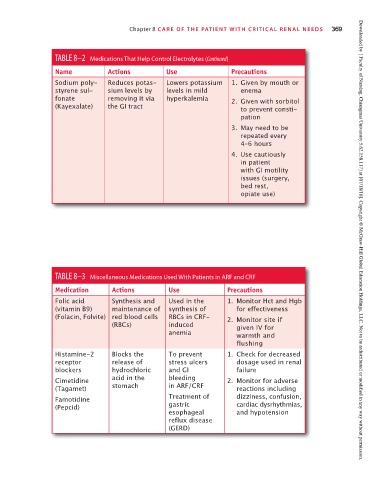
TABLE 8–2 Medications That Help Control Electrolytes (Continued)
Name Actions Use Precautions
Sodium poly- Reduces potas- Lowers potassium 1. Given by mouth or
styrene sul- sium levels by levels in mild enema
fonate removing it via hyperkalemia 2. Given with sorbitol
(Kayexalate) the GI tract to prevent consti-
pation
3. May need to be
repeated every
4–6 hours
4. Use cautiously
in patient
with GI motility
issues (surgery,
bed rest,
opiate use)
TABLE 8–3 Miscellaneous Medications Used With Patients in ARF and CRF Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
Medication Actions Use Precautions
Folic acid Synthesis and Used in the 1. Monitor Hct and Hgb
(vitamin B9) maintenance of synthesis of for effectiveness
(Folacin, Folvite) red blood cells RBCs in CRF- 2. Monitor site if
(RBCs) induced given IV for
anemia warmth and
flushing
Histamine-2 Blocks the To prevent 1. Check for decreased
receptor release of stress ulcers dosage used in renal
blockers hydrochloric and GI failure
Cimetidine acid in the bleeding 2. Monitor for adverse
(Tagamet) stomach in ARF/CRF reactions including
Famotidine Treatment of dizziness, confusion,
(Pepcid) gastric cardiac dysrhythmias,
esophageal and hypotension
reflux disease
(GERD)