Page 381 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 381
366 CRITICAL CARE NURSING DeMYSTIFIED
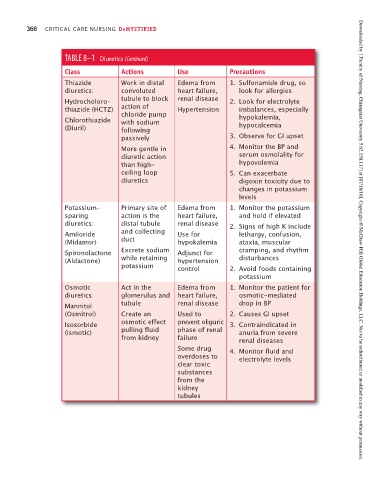
TABLE 8–1 Diuretics (Continued)
Class Actions Use Precautions
Thiazide Work in distal Edema from 1. Sulfonamide drug, so
diuretics: convoluted heart failure, look for allergies
Hydrocholoro- tubule to block renal disease 2. Look for electrolyte
thiazide (HCTZ) action of Hypertension imbalances, especially
chloride pump
Chlorothiazide with sodium hypokalemia,
(Diuril) following hypocalcemia
passively 3. Observe for GI upset
More gentle in 4. Monitor the BP and
diuretic action serum osmolality for
than high- hypovolemia
ceiling loop 5. Can exacerbate
diuretics digoxin toxicity due to
changes in potassium
levels
Potassium- Primary site of Edema from 1. Monitor the potassium
sparing action is the heart failure, and hold if elevated
diuretics: distal tubule renal disease 2. Signs of high K include
Amiloride and collecting Use for lethargy, confusion,
(Midamor) duct hypokalemia ataxia, muscular Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
Spironolactone Excrete sodium Adjunct for cramping, and rhythm
(Aldactone) while retaining hypertension disturbances
potassium control 2. Avoid foods containing
potassium
Osmotic Act in the Edema from 1. Monitor the patient for
diuretics: glomerulus and heart failure, osmotic-mediated
Mannitol tubule renal disease drop in BP
(Osmitrol) Create an Used to 2. Causes GI upset
Isosorbide osmotic effect prevent oliguric 3. Contraindicated in
(Ismotic) pulling fluid phase of renal anuria from severe
from kidney failure renal diseases
Some drug 4. Monitor fluid and
overdoses to electrolyte levels
clear toxic
substances
from the
kidney
tubules