Page 383 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 383
368 CRITICAL CARE NURSING DeMYSTIFIED
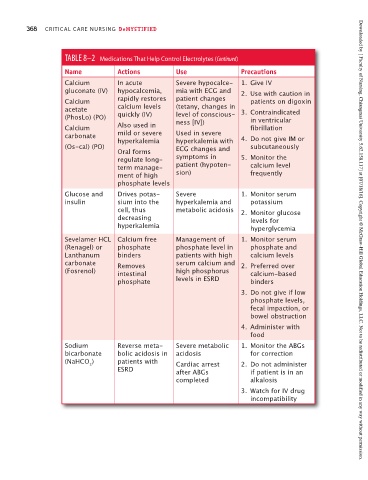
TABLE 8–2 Medications That Help Control Electrolytes (Continued)
Name Actions Use Precautions
Calcium In acute Severe hypocalce- 1. Give IV
gluconate (IV) hypocalcemia, mia with ECG and 2. Use with caution in
Calcium rapidly restores patient changes patients on digoxin
acetate calcium levels (tetany, changes in 3. Contraindicated
(PhosLo) (PO) quickly (IV) level of conscious- in ventricular
ness [IV])
Calcium Also used in fibrillation
carbonate mild or severe Used in severe
hyperkalemia hyperkalemia with 4. Do not give IM or
(Os-cal) (PO) ECG changes and subcutaneously
Oral forms
regulate long- symptoms in 5. Monitor the
term manage- patient (hypoten- calcium level
ment of high sion) frequently
phosphate levels
Glucose and Drives potas- Severe 1. Monitor serum
insulin sium into the hyperkalemia and potassium
cell, thus metabolic acidosis 2. Monitor glucose
decreasing levels for
hyperkalemia hyperglycemia
Sevelamer HCL Calcium free Management of 1. Monitor serum Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
(Renagel) or phosphate phosphate level in phosphate and
Lanthanum binders patients with high calcium levels
carbonate Removes serum calcium and 2. Preferred over
(Fosrenol) intestinal high phosphorus calcium-based
phosphate levels in ESRD binders
3. Do not give if low
phosphate levels,
fecal impaction, or
bowel obstruction
4. Administer with
food
Sodium Reverse meta- Severe metabolic 1. Monitor the ABGs
bicarbonate bolic acidosis in acidosis for correction
(NaHCO ) patients with Cardiac arrest 2. Do not administer
3
ESRD after ABGs if patient is in an
completed alkalosis
3. Watch for IV drug
incompatibility