Page 382 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 382
Chapter 8 CARE OF THE PATIENT WITH CRITICAL RENAL NEEDS 367
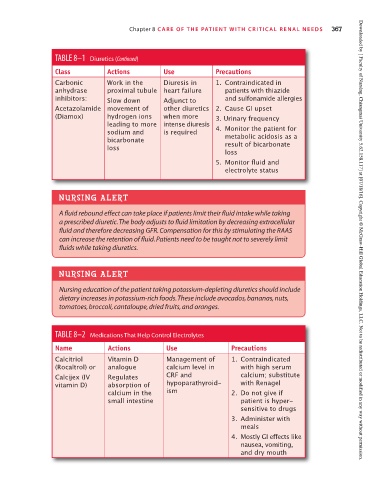
TABLE 8–1 Diuretics (Continued)
Class Actions Use Precautions
Carbonic Work in the Diuresis in 1. Contraindicated in
anhydrase proximal tubule heart failure patients with thiazide
inhibitors: Slow down Adjunct to and sulfonamide allergies
Acetazolamide movement of other diuretics 2. Cause GI upset
(Diamox) hydrogen ions when more 3. Urinary frequency
leading to more intense diuresis
sodium and is required 4. Monitor the patient for
bicarbonate metabolic acidosis as a
loss result of bicarbonate
loss
5. Monitor fluid and
electrolyte status
NURSING ALERT
A fluid rebound effect can take place if patients limit their fluid intake while taking
a prescribed diuretic. The body adjusts to fluid limitation by decreasing extracellular
fluid and therefore decreasing GFR. Compensation for this by stimulating the RAAS
can increase the retention of fluid. Patients need to be taught not to severely limit Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
fluids while taking diuretics.
NURSING ALERT
Nursing education of the patient taking potassium-depleting diuretics should include
dietary increases in potassium-rich foods. These include avocados, bananas, nuts,
tomatoes, broccoli, cantaloupe, dried fruits, and oranges.
TABLE 8–2 Medications That Help Control Electrolytes
Name Actions Use Precautions
Calcitriol Vitamin D Management of 1. Contraindicated
(Rocaltrol) or analogue calcium level in with high serum
Calcijex (IV Regulates CRF and calcium; substitute
vitamin D) absorption of hypoparathyroid- with Renagel
calcium in the ism 2. Do not give if
small intestine patient is hyper-
sensitive to drugs
3. Administer with
meals
4. Mostly GI effects like
nausea, vomiting,
and dry mouth