Page 435 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 435
420 CRITICAL CARE NURSING DeMYSTIFIED
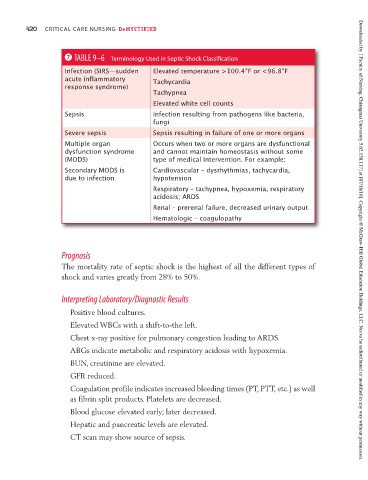
7 TABLE 9–6 Terminology Used in Septic Shock Classification
Infection (SIRS—sudden Elevated temperature >100.4°F or < 96.8°F
acute inflammatory Tachycardia
response syndrome)
Tachypnea
Elevated white cell counts
Sepsis Infection resulting from pathogens like bacteria,
fungi
Severe sepsis Sepsis resulting in failure of one or more organs
Multiple organ Occurs when two or more organs are dysfunctional
dysfunction syndrome and cannot maintain homeostasis without some
(MODS) type of medical intervention. For example:
Secondary MODS is Cardiovascular – dysrhythmias, tachycardia,
due to infection hypotension
Respiratory – tachypnea, hypoxemia, respiratory
acidosis; ARDS
Renal – prerenal failure, decreased urinary output
Hematologic – coagulopathy
Prognosis Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
The mortality rate of septic shock is the highest of all the different types of
shock and varies greatly from 28% to 50%.
Interpreting Laboratory/Diagnostic Results
Positive blood cultures.
Elevated WBCs with a shift-to-the left.
Chest x-ray positive for pulmonary congestion leading to ARDS.
ABGs indicate metabolic and respiratory acidosis with hypoxemia.
BUN, creatinine are elevated.
GFR reduced.
Coagulation profile indicates increased bleeding times (PT, PTT, etc.) as well
as fibrin split products. Platelets are decreased.
Blood glucose elevated early; later decreased.
Hepatic and pancreatic levels are elevated.
CT scan may show source of sepsis.