Page 431 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 431
416 CRITICAL CARE NURSING DeMYSTIFIED
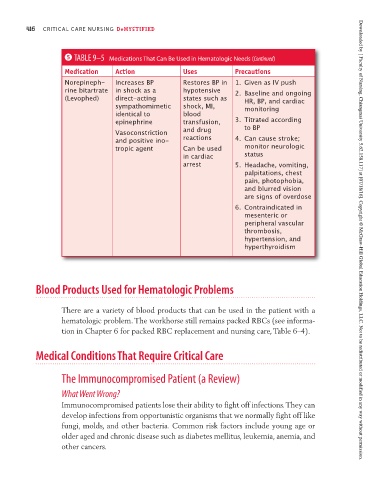
5 TABLE 9–5 Medications That Can Be Used in Hematologic Needs (Continued)
Medication Action Uses Precautions
Norepineph- Increases BP Restores BP in 1. Given as IV push
rine bitartrate in shock as a hypotensive 2. Baseline and ongoing
(Levophed) direct-acting states such as HR, BP, and cardiac
sympathomimetic shock, MI, monitoring
identical to blood
epinephrine transfusion, 3. Titrated according
Vasoconstriction and drug to BP
and positive ino- reactions 4. Can cause stroke;
tropic agent Can be used monitor neurologic
in cardiac status
arrest 5. Headache, vomiting,
palpitations, chest
pain, photophobia,
and blurred vision
are signs of overdose
6. Contraindicated in
mesenteric or
peripheral vascular
thrombosis,
hypertension, and Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
hyperthyroidism
Blood Products Used for Hematologic Problems
There are a variety of blood products that can be used in the patient with a
hematologic problem. The workhorse still remains packed RBCs (see informa-
tion in Chapter 6 for packed RBC replacement and nursing care, Table 6–4).
Medical Conditions That Require Critical Care
The Immunocompromised Patient (a Review)
What Went Wrong?
Immunocompromised patients lose their ability to fight off infections. They can
develop infections from opportunistic organisms that we normally fight off like
fungi, molds, and other bacteria. Common risk factors include young age or
older aged and chronic disease such as diabetes mellitus, leukemia, anemia, and
other cancers.