Page 130 - Color_Atlas_of_Physiology_5th_Ed._-_A._Despopoulos_2003
P. 130
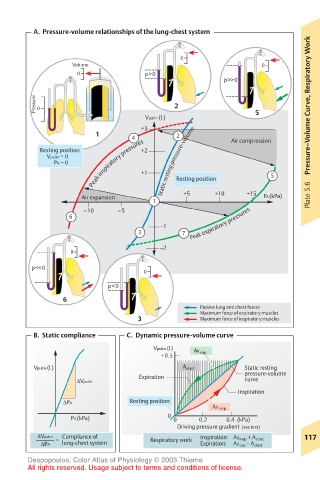
A. Pressure-volume relationships of the lung-chest system
0
Volume 0
0 p>0
p>>0
Pressure 0 2 Pressure–Volume Curve, Respiratory Work
Vpulm (L) 5
+3
1 4 2 Air compression
Resting position +2
Vpulm = 0
PA = 0 Peak inspiratory pressures +1 Static resting pressure-volume 5
Resting position
Air expansion +5 +10 +15 PA (kPa) Plate 5.6
1
–10 –5
6
–1 Peak expiratory pressures
3 7
–2
0
p<<0
0
p<0
6
Passive lung and chest forces
Maximum force of expiratory muscles
3 Maximum force of inspiratory muscles
B. Static compliance C. Dynamic pressure-volume curve
Vpulm (L)
+0.5 AR exp
Vpulm (L) A elast Static resting
Expiration pressure-volume
∆Vpulm curve
Inspiration
∆PA Resting position
AR insp
PA (kPa) 0 0 0.2 0.4 (kPa)
Driving pressure gradient (see text)
∆Vpulm Compliance of 117
= Respiratory work Inspiration: AR insp + A elast
∆PA lung-chest system Expiration: AR exp – A elast
Despopoulos, Color Atlas of Physiology © 2003 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.