Page 206 - Color_Atlas_of_Physiology_5th_Ed._-_A._Despopoulos_2003
P. 206
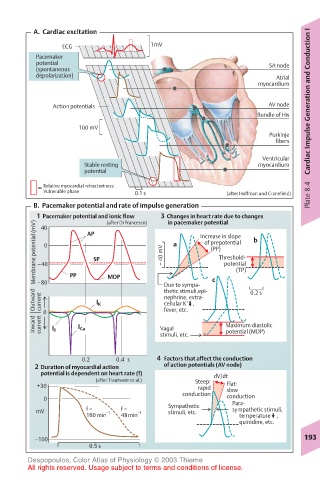
A. Cardiac excitation
ECG 1mV
Pacemaker
potential SA node
(spontaneous
depolarization) Atrial
myocardium
Action potentials AV node Cardiac Impulse Generation and Conduction I
Bundle of His
100 mV
Purkinje
fibers
Ventricular
Stable resting myocardium
potential
Relative myocardial refractoriness:
Vulnerable phase 0.1 s (after Hoffman und Cranefield) Plate 8.4
B. Pacemaker potential and rate of impulse generation
1 Pacemaker potential and ionic flow 3 Changes in heart rate due to changes
in pacemaker potential
(after Di Francesco)
Membrane potential (mV) –40 0 PP SP – 40 mV a Increase in slope b
40
AP
of prepotential
(PP)
Threshold-
potential
(TP)
thetic stimuli,epi-
Outward –80 I K MDP Due to sympa- c 0.2 s
current
nephrine, extra-
+
cellular K
,
0 fever, etc.
Inward current I Ca Vagal Maximum diastolic
I f
stimuli, etc. potential (MDP)
0.2 0.4 s 4 Factors that affect the conduction
2 Duration of myocardial action of action potentials (AV node)
potential is dependent on heart rate (f) dV/dt
(after Trautwein et al.) Steep:
+30 rapid Flat:
conduction slow
0 conduction
Sympathetic Para-
mV f = –1 f = –1 stimuli, etc. sympathetic stimuli,
160min 48min temperature ,
quinidine, etc.
–100 193
0.5 s
Despopoulos, Color Atlas of Physiology © 2003 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.