Page 246 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 246
150 PART 2: General Management of the Patient
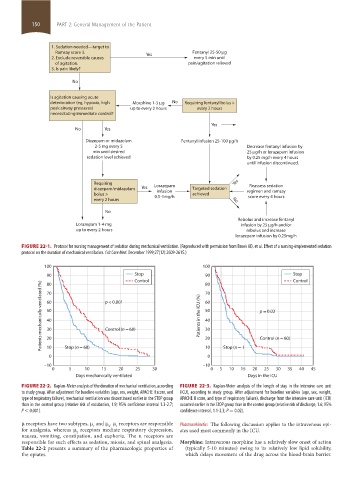
1. Sedation needed—target to
Ramsay score 3. Yes Fentanyl 25-50 g
2. Exclude reversible causes every 5 min until
of agitation. pain/agitation relieved
3. Is pain likely?
No
Is agitation causing acute
deterioration (eg, hypoxia, high Morphine 1-5 g No Requiring fentanyl bolus >
peak airway pressures) up to every 2 hours every 2 hours
necessitating immediate control?
Yes
No Yes
Diazepam or midazolam Fentanyl infusion 25-100 g/h
2-5 mg every 5 Decrease fentanyl infusion by
min until desired 25 g/h or lorazepam infusion
sedation level achieved by 0.25 mg/h every 4 hours
until infusion discontinued.
Requiring Lorazepam Yes Reassess sedation
diazepam/midazolam Yes infusion Targeted sedation regimen and ramsay
bolus > 0.5-1mg/h achieved score every 4 hours
every 2 hours No
No
Rebolus and increase fentanyl
Lorazepam 1-4 mg infusion by 25 g/h and/or
up to every 2 hours rebolus and increase
lorazepam infusion by 0.25mg/h
FIGURE 22-1. Protocol for nursing management of sedation during mechanical ventilation. (Reproduced with permission from Brook AD, et al. Effect of a nursing-implemented sedation
protocol on the duration of mechanical ventilation. Crit Care Med. December 1999;27(12):2609-2615.)
100 100
90 Stop 90 Stop
Control 80 Control
Patients mechanically ventilated (%) 60 p < 0.001 Patients in the ICU (%) 60 p = 0.02
80
70
70
50
50
40
40
Control (n = 60)
30
30
20
10
10
0 Stop (n = 68) 20 0 Stop (n = ) Control (n = 60)
–10 –10
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45
Days mechanically ventilated Days in the ICU
FIGURE 22-2. Kaplan-Meier analysis of the duration of mechanical ventilation, according FIGURE 22-3. Kaplan-Meier analysis of the length of stay in the intensive care unit
to study group. After adjustment for baseline variables (age, sex, weight, APACHE II score, and (ICU), according to study group. After adjustment for baseline variables (age, sex, weight,
type of respiratory failure), mechanical ventilation was discontinued earlier in the STOP group APACHE II score, and type of respiratory failure), discharge from the intensive care unit (ICU)
than in the control group (relative risk of extubation, 1.9; 95% confidence interval 1.3-2.7; occurred earlier in the STOP group than in the control group (relative risk of discharge, 1.6; 95%
P < 0.001). confidence interval, 1.1-2.3; P = 0.02).
μ receptors have two subtypes, μ and μ . μ receptors are responsible Pharmacokinetics The following discussion applies to the intravenous opi-
2
1
1
for analgesia, whereas μ receptors mediate respiratory depression, ates used most commonly in the ICU.
2
nausea, vomiting, constipation, and euphoria. The κ receptors are
responsible for such effects as sedation, miosis, and spinal analgesia. Morphine: Intravenous morphine has a relatively slow onset of action
Table 22-2 presents a summary of the pharmacologic properties of (typically 5-10 minutes) owing to its relatively low lipid solubility,
the opiates. which delays movement of the drug across the blood-brain barrier.
section02.indd 150 1/13/2015 2:05:04 PM