Page 86 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 86
54 PART 1: An Overview of the Approach to and Organization of Critical Care
TABLE 8-2 The Standards for Coding and Responsible Maintenance Organizations
Standard Functionality Maintainer URL
International Classification of Diseases, 9th ICD-9 published by World Health Organization in 1977 and The National Center for Health Statistics http://www.cdc.gov/nchs
Edition, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM) currently in public domain. ICD-9-CM, clinical modification (NCHS) of Centers for Disease Control (CDC)
currently in use in the United States and extended with
additional morbidity details and procedures codes
National Drug Codes (NDC) Product identifiers for human drugs. The current edition of National Council for Prescription Drug http://www.ncpdp.org
the National Drug Code Directory is limited to prescription Programs (NCPDP)
drugs and a few selected over-the-counter products
Healthcare Common Procedure Coding Code set for reporting supplies, orthotic and prosthetic Center for Medicare and Medicaid Service http://www.cms.gov
System (HCPCS) devices, and durable medical equipment (CMS)
Current Procedural Terminology, Fourth Medical nomenclature used to report medical procedures American Medical Association (AMA), National http://www.ama-assn.org
Edition (CPT-4) and services under public and private health insurance Uniform Billing Committee (NUBC), and
programs National Uniform Claim Committee (NUCC)
Code on Dental Procedures and Nomenclature Used to record and report dental procedures and treatment Dental Content Committee of the American http://www.ada.org
(CDT) Dental Association (ADA DCC)
Health Level Seven (HL7), Clinical Document Submission of lab results and patient summaries to public HL7 International http://www.hl7.org
Architecture (CDA), Continuity of Care health agencies for surveillance or reporting (excluding
Document (CCD) adverse events reporting); submitting information to
immunization registries
(3) Identifiers, and (4) Transactions and Code Sets (HIPAA TCS rule).
The HIPAA TCS Rule took effect in October 2003 and includes eight Cohort
ANSI X12N standards (http://www.x12.org/). The Secretary of the Information Dashboards
Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) operates the stan- Identification
dards maintenance organizations (DMSO) and takes responsibilities for & Searching
the development, maintenance, and modification of relevant electronic Research Provider Reports
Cohorts
data interchange standards (Table 8-2). Profiling
During past decades, a number of controlled terminologies have been Quality Reports
developed including Clinical
• Digital imaging and communications in medicine (DICOM) Pharmaco- Genomic Research Applications Reporting Public
(http://medical.nema.org/): A standard developed for handling, Genomics
storing, printing, and transmitting information of medical imaging
by the joint committee of the American College of Radiology and the AHR
National Electrical Manufacturers Association. DICOM is vendor Pay for
independent. Current version is DICOM 3.0. Version 3 of DICOM Population Research Applications Performance
defines image data as well as patient, study, and visit information Research
necessary to provide the context for the images.
Chronic
• Systematized nomenclature of medicine—clinical terms IT Disease
(SNOMED CT): Comprehensive multilingual clinical terminology. Interventions Management
In 2010, National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) pub- Closed-
lished a set of approved procedures for testing information technology Clinical Loop (EMR)
systems that work with EHRs. This document is step forward to stan- Trials Work Flow
dardization of EMR.
■ SECONDARY DATA USE FOR PRACTICE MONITORING AND RESEARCH
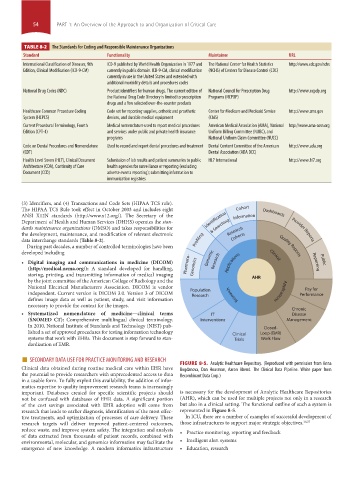
Clinical data obtained during routine medical care within EHR have FIGURE 8-5. Analytic Healthcare Repository. (Reproduced with permission from Anna
Bogdanova, Dan Housman, Aaron Abend. The Clinical Data Pipeline. White paper from
the potential to provide researchers with unprecedented access to data Recombinant Data Corp.)
in a usable form. To fully exploit this availability, the addition of infor-
matics expertise to quality improvement research teams is increasingly
important. Databases created for specific scientific projects should is necessary for the development of Analytic Healthcare Repositories
not be confused with databases of EHR data. A significant portion (AHR), which can be used for multiple projects not only in a research
of the cost savings associated with EHR adoption will come from but also in a clinical setting. The functional outline of such a system is
research that leads to earlier diagnosis, identification of the most effec- represented in Figure 8-5.
tive treatments, and optimization of processes of care delivery. These In ICU, there are a number of examples of successful development of
research targets will deliver improved patient-centered outcomes, those infrastructures to support major strategic objectives. 26,27
reduce waste, and improve system safety. The integration and analysis • Practice monitoring, reporting and feedback
of data extracted from thousands of patient records, combined with
environmental, molecular, and genomics information may facilitate the • Intelligent alert systems
emergence of new knowledge. A modern informatics infrastructure • Education, research
Section01.indd 54 1/22/2015 9:37:03 AM