Page 114 - Clinical Anatomy
P. 114
ECA2 7/18/06 6:42 PM Page 99
The gastrointestinal adnexae 99
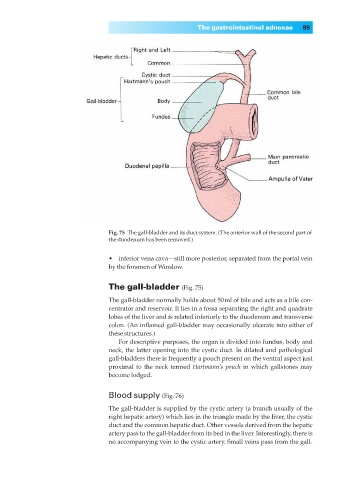
Fig. 75◊The gall-bladder and its duct system. (The anterior wall of the second part of
the duodenum has been removed.)
•◊◊inferior vena cava—still more posterior, separated from the portal vein
by the foramen of Winslow.
The gall-bladder (Fig. 75)
The gall-bladder normally holds about 50ml of bile and acts as a bile con-
centrator and reservoir. It lies in a fossa separating the right and quadrate
lobes of the liver and is related inferiorly to the duodenum and transverse
colon. (An inflamed gall-bladder may occasionally ulcerate into either of
these structures.)
For descriptive purposes, the organ is divided into fundus, body and
neck, the latter opening into the cystic duct. In dilated and pathological
gall-bladders there is frequently a pouch present on the ventral aspect just
proximal to the neck termed Hartmann’s pouch in which gallstones may
become lodged.
Blood supply (Fig. 76)
The gall-bladder is supplied by the cystic artery (a branch usually of the
right hepatic artery) which lies in the triangle made by the liver, the cystic
duct and the common hepatic duct. Other vessels derived from the hepatic
artery pass to the gall-bladder from its bed in the liver. Interestingly, there is
no accompanying vein to the cystic artery. Small veins pass from the gall-