Page 167 - Clinical Anatomy
P. 167
ECA2 7/18/06 6:43 PM Page 152
152 The abdomen and pelvis
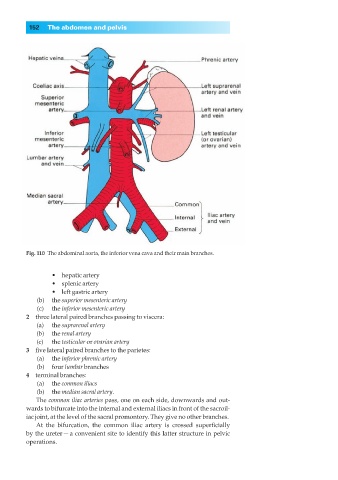
Fig. 110◊The abdominal aorta, the inferior vena cava and their main branches.
•◊◊hepatic artery
•◊◊splenic artery
•◊◊left gastric artery
(b) the superior mesenteric artery
(c) the inferior mesenteric artery
2◊◊three lateral paired branches passing to viscera:
(a) the suprarenal artery
(b) the renal artery
(c) the testicular or ovarian artery
3◊◊five lateral paired branches to the parietes:
(a) the inferior phrenic artery
(b) four lumbar branches
4◊◊terminal branches:
(a) the common iliacs
(b) the median sacral artery.
The common iliac arteries pass, one on each side, downwards and out-
wards to bifurcate into the internal and external iliacs in front of the sacroil-
iac joint, at the level of the sacral promontory. They give no other branches.
At the bifurcation, the common iliac artery is crossed superficially
by the ureter — a convenient site to identify this latter structure in pelvic
operations.