Page 169 - Clinical Anatomy
P. 169
ECA2 7/18/06 6:43 PM Page 154
154 The abdomen and pelvis
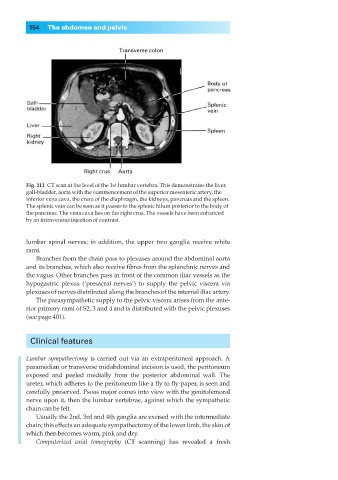
Fig. 111◊CT scan at the level of the 1st lumbar vertebra. This demonstrates the liver,
gall-bladder, aorta with the commencement of the superior mesenteric artery, the
inferior vena cava, the crura of the diaphragm, the kidneys, pancreas and the spleen.
The splenic vein can be seen as it passes to the splenic hilum posterior to the body of
the pancreas. The vena cava lies on the right crus. The vessels have been enhanced
by an intravenous injection of contrast.
lumbar spinal nerves; in addition, the upper two ganglia receive white
rami.
Branches from the chain pass to plexuses around the abdominal aorta
and its branches, which also receive fibres from the splanchnic nerves and
the vagus. Other branches pass in front of the common iliac vessels as the
hypogastric plexus (‘presacral nerves’) to supply the pelvic viscera via
plexuses of nerves distributed along the branches of the internal iliac artery.
The parasympathetic supply to the pelvic viscera arises from the ante-
rior primary rami of S2, 3 and 4 and is distributed with the pelvic plexuses
(see page 401).
Clinical features
Lumbar sympathectomy is carried out via an extraperitoneal approach. A
paramedian or transverse midabdominal incision is used, the peritoneum
exposed and peeled medially from the posterior abdominal wall. The
ureter, which adheres to the peritoneum like a fly to fly-paper, is seen and
carefully preserved. Psoas major comes into view with the genitofemoral
nerve upon it, then the lumbar vertebrae, against which the sympathetic
chain can be felt.
Usually the 2nd, 3rd and 4th ganglia are excised with the intermediate
chain; this effects an adequate sympathectomy of the lower limb, the skin of
which then becomes warm, pink and dry.
Computerized axial tomography (CT scanning) has revealed a fresh