Page 176 - Clinical Anatomy
P. 176
ECA3 7/18/06 6:44 PM Page 161
The female breast 161
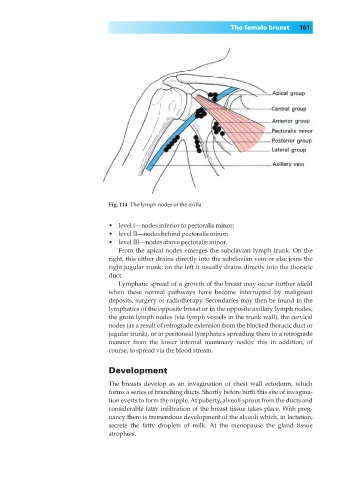
Fig. 114◊The lymph nodes of the axilla.
•◊◊level I—nodes inferior to pectoralis minor;
•◊◊level II—nodes behind pectoralis minor;
•◊◊level III—nodes above pectoralis minor.
From the apical nodes emerges the subclavian lymph trunk. On the
right, this either drains directly into the subclavian vein or else joins the
right jugular trunk; on the left it usually drains directly into the thoracic
duct.
Lymphatic spread of a growth of the breast may occur further afield
when these normal pathways have become interrupted by malignant
deposits, surgery or radiotherapy. Secondaries may then be found in the
lymphatics of the opposite breast or in the opposite axillary lymph nodes,
the groin lymph nodes (via lymph vessels in the trunk wall), the cervical
nodes (as a result of retrograde extension from the blocked thoracic duct or
jugular trunk), or in peritoneal lymphatics spreading there in a retrograde
manner from the lower internal mammary nodes: this in addition, of
course, to spread via the blood stream.
Development
The breasts develop as an invagination of chest wall ectoderm, which
forms a series of branching ducts. Shortly before birth this site of invagina-
tion everts to form the nipple. At puberty, alveoli sprout from the ducts and
considerable fatty infiltration of the breast tissue takes place. With preg-
nancy there is tremendous development of the alveoli which, in lactation,
secrete the fatty droplets of milk. At the menopause the gland tissue
atrophies.