Page 36 - Clinical Anatomy
P. 36
ECA1 7/18/06 6:31 PM Page 21
The lower respiratory tract 21
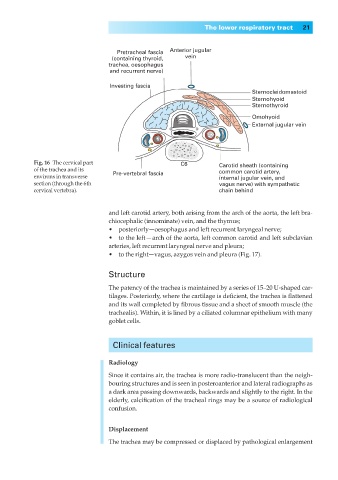
Pretracheal fascia Anterior jugular
(containing thyroid, vein
trachea, oesophagus
and recurrent nerve)
Investing fascia
Sternocleidomastoid
Sternohyoid
Sternothyroid
Omohyoid
External jugular vein
Fig. 16◊The cervical part C6 Carotid sheath (containing
of the trachea and its Pre-vertebral fascia common carotid artery,
environs in transverse internal jugular vein, and
section (through the 6th vagus nerve) with sympathetic
cervical vertebra). chain behind
and left carotid artery, both arising from the arch of the aorta, the left bra-
chiocephalic (innominate) vein, and the thymus;
•◊◊posteriorly—oesophagus and left recurrent laryngeal nerve;
•◊◊to the left — arch of the aorta, left common carotid and left subclavian
arteries, left recurrent laryngeal nerve and pleura;
•◊◊to the right—vagus, azygos vein and pleura (Fig. 17).
Structure
The patency of the trachea is maintained by a series of 15–20 U-shaped car-
tilages. Posteriorly, where the cartilage is deficient, the trachea is flattened
and its wall completed by fibrous tissue and a sheet of smooth muscle (the
trachealis). Within, it is lined by a ciliated columnar epithelium with many
goblet cells.
Clinical features
Radiology
Since it contains air, the trachea is more radio-translucent than the neigh-
bouring structures and is seen in posteroanterior and lateral radiographs as
a dark area passing downwards, backwards and slightly to the right. In the
elderly, calcification of the tracheal rings may be a source of radiological
confusion.
Displacement
The trachea may be compressed or displaced by pathological enlargement