Page 398 - Clinical Anatomy
P. 398
ECA6 7/18/06 6:54 PM Page 383
The special senses 383
The special senses
The nose (see also ‘The accessory nasal sinuses’, page 318)
The external nose consists of a bony and cartilaginous framework closely
overlaid by skin and fibrofatty tissues. The bones are the two nasal bones
and the frontal processes of the maxilla. The ala is composed solely of fatty
tissue at its lower free edge.
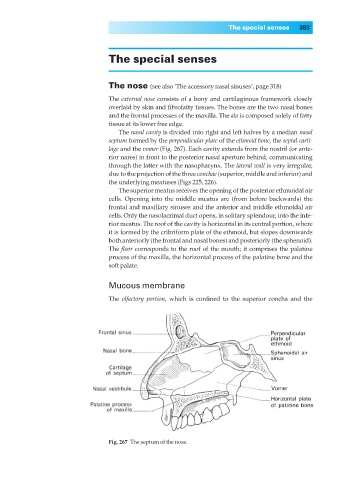
The nasal cavity is divided into right and left halves by a median nasal
septum formed by the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone, the septal carti-
lage and the vomer (Fig. 267). Each cavity extends from the nostril (or ante-
rior nares) in front to the posterior nasal aperture behind, communicating
through the latter with the nasopharynx. The lateral wall is very irregular,
due to the projection of the three conchae (superior, middle and inferior) and
the underlying meatuses (Figs 225, 226).
The superior meatus receives the opening of the posterior ethmoidal air
cells. Opening into the middle meatus are (from before backwards) the
frontal and maxillary sinuses and the anterior and middle ethmoidal air
cells. Only the nasolacrimal duct opens, in solitary splendour, into the infe-
rior meatus. The roof of the cavity is horizontal in its central portion, where
it is formed by the cribriform plate of the ethmoid, but slopes downwards
both anteriorly (the frontal and nasal bones) and posteriorly (the sphenoid).
The floor corresponds to the roof of the mouth; it comprises the palatine
process of the maxilla, the horizontal process of the palatine bone and the
soft palate.
Mucous membrane
The olfactory portion, which is confined to the superior concha and the
Fig. 267◊The septum of the nose.