Page 54 - Clinical Anatomy
P. 54
ECA1 7/18/06 6:31 PM Page 39
The mediastinum 39
Left common
carotid artery
Brachiocephalic Left subclavian
artery artery
Right pulmonary
artery Ductus arteriosus
Aorta
Left pulmonary
Superior artery
vena cava
Septum II
Pulmonary trunk
Foramen ovale
Septum I
Aorta
Inferior
vena cava
Umbilical arteries
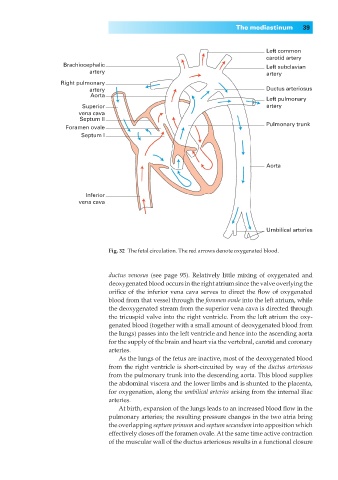
Fig. 32◊The fetal circulation. The red arrows denote oxygenated blood.
ductus venosus (see page 95). Relatively little mixing of oxygenated and
deoxygenated blood occurs in the right atrium since the valve overlying the
orifice of the inferior vena cava serves to direct the flow of oxygenated
blood from that vessel through the foramen ovale into the left atrium, while
the deoxygenated stream from the superior vena cava is directed through
the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle. From the left atrium the oxy-
genated blood (together with a small amount of deoxygenated blood from
the lungs) passes into the left ventricle and hence into the ascending aorta
for the supply of the brain and heart via the vertebral, carotid and coronary
arteries.
As the lungs of the fetus are inactive, most of the deoxygenated blood
from the right ventricle is short-circuited by way of the ductus arteriosus
from the pulmonary trunk into the descending aorta. This blood supplies
the abdominal viscera and the lower limbs and is shunted to the placenta,
for oxygenation, along the umbilical arteries arising from the internal iliac
arteries.
At birth, expansion of the lungs leads to an increased blood flow in the
pulmonary arteries; the resulting pressure changes in the two atria bring
the overlapping septum primum and septum secundum into apposition which
effectively closes off the foramen ovale. At the same time active contraction
of the muscular wall of the ductus arteriosus results in a functional closure