Page 121 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 121
Operating Modes of Mechanical Ventilation 87
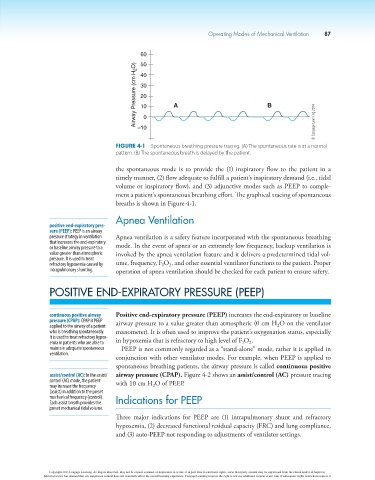
60
50
Airway Pressure (cm H 2 O) 40 A B
30
20
10
© Cengage Learning 2014
0
–10
Figure 4-1 Spontaneous breathing pressure tracing. (A) The spontaneous rate is at a normal
pattern. (B) The spontaneous breath is delayed by the patient.
the spontaneous mode is to provide the (1) inspiratory flow to the patient in a
timely manner, (2) flow adequate to fulfill a patient’s inspiratory demand (i.e., tidal
volume or inspiratory flow), and (3) adjunctive modes such as PEEP to comple-
ment a patient’s spontaneous breathing effort. The graphical tracing of spontaneous
breaths is shown in Figure 4-1.
Apnea Ventilation
positive end-expiratory pres-
sure (PEEP): PEEP is an airway
pressure strategy in ventilation Apnea ventilation is a safety feature incorporated with the spontaneous breathing
that increases the end-expiratory
or baseline airway pressure to a mode. In the event of apnea or an extremely low frequency, backup ventilation is
value greater than atmospheric invoked by the apnea ventilation feature and it delivers a predetermined tidal vol-
pressure. It is used to treat
refractory hypoxemia caused by ume, frequency, F O , and other essential ventilator functions to the patient. Proper
I
2
intrapulmonary shunting. operation of apnea ventilation should be checked for each patient to ensure safety.
POSITIVE END-EXPIRATORY PRESSURE (PEEP)
continuous positive airway Positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) increases the end-expiratory or baseline
pressure (CPAP): CPAP is PEEP airway pressure to a value greater than atmospheric (0 cm H O on the ventilator
applied to the airway of a patient 2
who is breathing spontaneously. manometer). It is often used to improve the patient’s oxygenation status, especially
It is used to treat refractory hypox-
emia in patients who are able to in hypoxemia that is refractory to high level of F O .
I
2
maintain adequate spontaneous PEEP is not commonly regarded as a “stand-alone” mode, rather it is applied in
ventilation.
conjunction with other ventilator modes. For example, when PEEP is applied to
spontaneous breathing patients, the airway pressure is called continuous positive
assist/control (AC): In the assist/ airway pressure (CPAP). Figure 4-2 shows an assist/control (AC) pressure tracing
control (AC) mode, the patient with 10 cm H O of PEEP.
may increase the frequency 2
(assist) in addition to the preset
mechanical frequency (control). Indications for PEEP
Each assist breath provides the
preset mechanical tidal volume.
Three major indications for PEEP are (1) intrapulmonary shunt and refractory
hypoxemia, (2) decreased functional residual capacity (FRC) and lung compliance,
and (3) auto-PEEP not responding to adjustments of ventilator settings.
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.