Page 122 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 122
88 Chapter 4
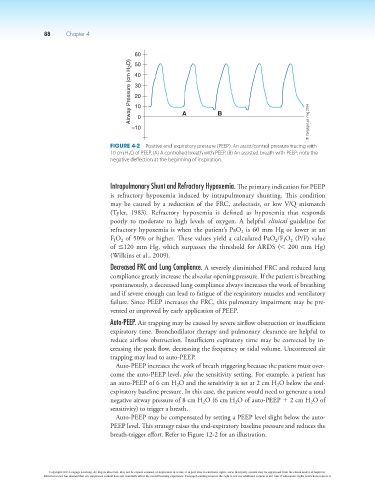
60
Airway Pressure (cm H 2 O) 40
50
30
20
10
0
–10 A B © Cengage Learning 2014
Figure 4-2 Positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP). An assist/control pressure tracing with
10 cm H 2 O of PEEP. (A) A controlled breath with PEEP. (B) An assisted breath with PEEP; note the
negative deflection at the beginning of inspiration.
Intrapulmonary Shunt and Refractory Hypoxemia. The primary indication for PEEP
is refractory hypoxemia induced by intrapulmonary shunting. This condition
may be caused by a reduction of the FRC, atelectasis, or low V/Q mismatch
(Tyler, 1983). Refractory hypoxemia is defined as hypoxemia that responds
poorly to moderate to high levels of oxygen. A helpful clinical guideline for
refractory hypoxemia is when the patient’s PaO is 60 mm Hg or lower at an
2
F O of 50% or higher. These values yield a calculated PaO /F O (P/F) value
I
2
I
2
2
of #120 mm Hg, which surpasses the threshold for ARDS (, 200 mm Hg)
(Wilkins et al., 2009).
Decreased FRC and Lung Compliance. A severely diminished FRC and reduced lung
compliance greatly increase the alveolar opening pressure. If the patient is breathing
spontaneously, a decreased lung compliance always increases the work of breathing
and if severe enough can lead to fatigue of the respiratory muscles and ventilatory
failure. Since PEEP increases the FRC, this pulmonary impairment may be pre-
vented or improved by early application of PEEP.
Auto-PEEP. Air trapping may be caused by severe airflow obstruction or insufficient
expiratory time. Bronchodilator therapy and pulmonary clearance are helpful to
reduce airflow obstruction. Insufficient expiratory time may be corrected by in-
creasing the peak flow, decreasing the frequency or tidal volume. Uncorrected air
trapping may lead to auto-PEEP.
Auto-PEEP increases the work of breath triggering because the patient must over-
come the auto-PEEP level, plus the sensitivity setting. For example, a patient has
an auto-PEEP of 6 cm H O and the sensitivity is set at 2 cm H O below the end-
2
2
expiratory baseline pressure. In this case, the patient would need to generate a total
negative airway pressure of 8 cm H O (6 cm H O of auto-PEEP 1 2 cm H O of
2
2
2
sensitivity) to trigger a breath.
Auto-PEEP may be compensated by setting a PEEP level slight below the auto-
PEEP level. This strategy raises the end-expiratory baseline pressure and reduces the
breath-trigger effort. Refer to Figure 12-2 for an illustration.
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.