Page 337 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 337
Hemodynamic Monitoring 303
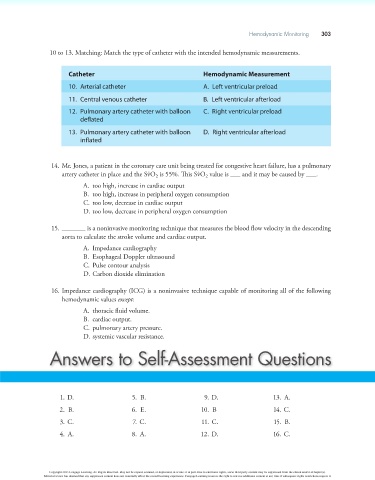
10 to 13. Matching: Match the type of catheter with the intended hemodynamic measurements.
Catheter Hemodynamic Measurement
10. Arterial catheter A. Left ventricular preload
11. Central venous catheter B. Left ventricular afterload
12. Pulmonary artery catheter with balloon C. Right ventricular preload
deflated
13. Pulmonary artery catheter with balloon D. Right ventricular afterload
inflated
14. Mr. Jones, a patient in the coronary care unit being treated for congestive heart failure, has a pulmonary
#
#
artery catheter in place and the SvO is 55%. This SvO value is ___ and it may be caused by ___.
2
2
A. too high, increase in cardiac output
B. too high, increase in peripheral oxygen consumption
C. too low, decrease in cardiac output
D. too low, decrease in peripheral oxygen consumption
15. _______ is a noninvasive monitoring technique that measures the blood flow velocity in the descending
aorta to calculate the stroke volume and cardiac output.
A. Impedance cardiography
B. Esophageal Doppler ultrasound
C. Pulse contour analysis
D. Carbon dioxide elimination
16. Impedance cardiography (ICG) is a noninvasive technique capable of monitoring all of the following
hemodynamic values except:
A. thoracic fluid volume.
B. cardiac output.
C. pulmonary artery pressure.
D. systemic vascular resistance.
Answers to Self-Assessment Questions
1. D. 5. B. 9. D. 13. A.
2. B. 6. E. 10. B 14. C.
3. C. 7. C. 11. C. 15. B.
4. A. 8. A. 12. D. 16. C.
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.