Page 526 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 526
492 Chapter 15
The criteria for ALI and ARDS are same with the exception of the PaO /F O values
I
2
2
ARDS is a more severe (#300 mm Hg for ALI and #200 mm Hg for ARDS—regardless of PEEP level
form of ALI. The PaO 2 /F I O 2
threshold for ALI is # 300 for ALI and ARDS). When using the PaO /F O as an evaluation tool for ALI and
2
2
I
mm Hg, and for ARDS it is
# 200 mm Hg. ARDS, it is essential to consider other conditions that may contribute to the decrease
of PaO /F O . For example, hypoventilation can lower the PaO and PaO /F O .
2
2
I
2
2
2
I
Pathophysiology
The alveolar-capillary membrane consists of the alveolar epithelium and the vascu-
Direct injury to the lungs
can lead to pathological ab- lar endothelium. Research studies have shown that damage to the lungs can occur
normality in the intra-alveolar
space and alveolar filling on either side of the membrane.
by edema, fibrin, collagen,
neutrophilic aggregates, or Direct Injury. Exposure of alveolar epithelium to direct insult (e.g., bacteria) leads
blood. to activation of alveolar macrophages and development of inflammatory response
within the lungs. Furthermore, alveolar epithelial damage can lead to pathological
abnormality in the intra-alveolar space and alveolar filling by edema, fibrin, col-
lagen, neutrophilic aggregates, or blood (Johanson et al., 1985; Paolo et al., 1993;
Indirect injury to the
lungs primarily lead to Rocco et al., 2008). The radiographic signs of ALI typically show infiltrates and
microvascular congestion
and interstitial edema, with pulmonary consolidation. Clinical conditions that are associated with direct lung
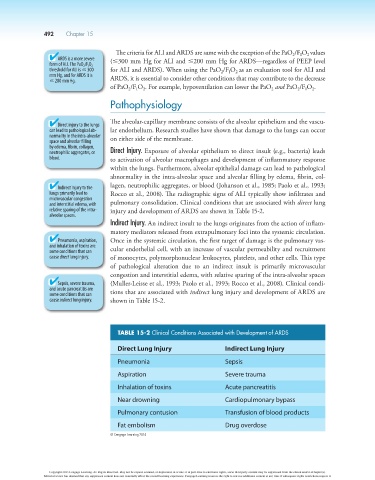
relative sparing of the intra- injury and development of ARDS are shown in Table 15-2.
alveolar spaces.
Indirect Injury. An indirect insult to the lungs originates from the action of inflam-
matory mediators released from extrapulmonary foci into the systemic circulation.
Pneumonia, aspiration, Once in the systemic circulation, the first target of damage is the pulmonary vas-
and inhalation of toxins are
some conditions that can cular endothelial cell, with an increase of vascular permeability and recruitment
cause direct lung injury. of monocytes, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, platelets, and other cells. This type
of pathological alteration due to an indirect insult is primarily microvascular
congestion and interstitial edema, with relative sparing of the intra-alveolar spaces
Sepsis, severe trauma, (Muller-Leisse et al., 1993; Paolo et al., 1993; Rocco et al., 2008). Clinical condi-
and acute pancreatitis are
some conditions that can tions that are associated with indirect lung injury and development of ARDS are
cause indirect lung injury. shown in Table 15-2.
TABLE 15-2 Clinical Conditions Associated with Development of ARDS
Direct Lung Injury Indirect Lung Injury
Pneumonia Sepsis
Aspiration Severe trauma
Inhalation of toxins Acute pancreatitis
Near drowning Cardiopulmonary bypass
Pulmonary contusion Transfusion of blood products
Fat embolism Drug overdose
© Cengage Learning 2014
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.