Page 530 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 530
496 Chapter 15
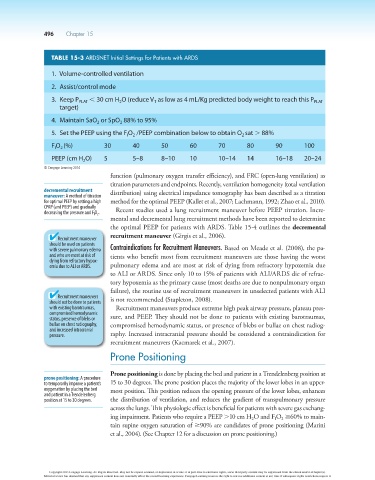
TABLE 15-3 ARDSnET Initial Settings for Patients with ARDS
1. Volume-controlled ventilation
2. Assist/control mode
3. Keep P PLAT , 30 cm H O (reduce V as low as 4 mL/Kg predicted body weight to reach this P PLAT
2
T
target)
4. Maintain SaO or SpO 88% to 95%
2
2
5. Set the PEEP using the F O /PEEP combination below to obtain O sat . 88%
2
2
I
F O (%) 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
I
2
PEEP (cm H O) 5 5–8 8–10 10 10–14 14 16–18 20–24
2
© Cengage Learning 2014
function (pulmonary oxygen transfer efficiency), and FRC (open-lung ventilation) as
titration parameters and endpoints. Recently, ventilation homogeneity (total ventilation
decremental recruitment distribution) using electrical impedance tomography has been described as a titration
maneuver: A method of titration
for optimal PEEP by setting a high method for the optimal PEEP (Kallet et al., 2007; Lachmann, 1992; Zhao et al., 2010).
CPAP (and PEEP) and gradually
decreasing the pressure and F I O 2 . Recent studies used a lung recruitment maneuver before PEEP titration. Incre-
mental and decremental lung recruitment methods have been reported to determine
the optimal PEEP for patients with ARDS. Table 15-4 outlines the decremental
recruitment maneuver (Girgis et al., 2006).
Recruitment maneuver
should be used on patients
with severe pulmonary edema Contraindications for Recruitment Maneuvers. Based on Meade et al. (2008), the pa-
and who are most at risk of tients who benefit most from recruitment maneuvers are those having the worst
dying from refractory hypox-
emia due to ALI or ARDS. pulmonary edema and are most at risk of dying from refractory hypoxemia due
to ALI or ARDS. Since only 10 to 15% of patients with ALI/ARDS die of refrac-
tory hypoxemia as the primary cause (most deaths are due to nonpulmonary organ
failure), the routine use of recruitment maneuvers in unselected patients with ALI
Recruitment maneuvers is not recommended (Stapleton, 2008).
should not be done to patients
with existing barotraumas, Recruitment maneuvers produce extreme high peak airway pressure, plateau pres-
compromised hemodynamic
status, presence of blebs or sure, and PEEP. They should not be done to patients with existing barotraumas,
bullae on chest radiography, compromised hemodynamic status, or presence of blebs or bullae on chest radiog-
and increased intracranial
pressure. raphy. Increased intracranial pressure should be considered a contraindication for
recruitment maneuvers (Kacmarek et al., 2007).
Prone Positioning
Prone positioning is done by placing the bed and patient in a Trendelenberg position at
prone positioning: A procedure
to temporarily improve a patient’s 15 to 30 degrees. The prone position places the majority of the lower lobes in an upper-
oxygenation by placing the bed most position. This position reduces the opening pressure of the lower lobes, enhances
and patient in a Trendelenberg
position at 15 to 30 degrees. the distribution of ventilation, and reduces the gradient of transpulmonary pressure
across the lungs. This physiologic effect is beneficial for patients with severe gas exchang-
ing impairment. Patients who require a PEEP .10 cm H O and F O $60% to main-
2
I
2
tain supine oxygen saturation of $90% are candidates of prone positioning (Marini
et al., 2004). (See Chapter 12 for a discussion on prone positioning.)
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.