Page 599 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 599
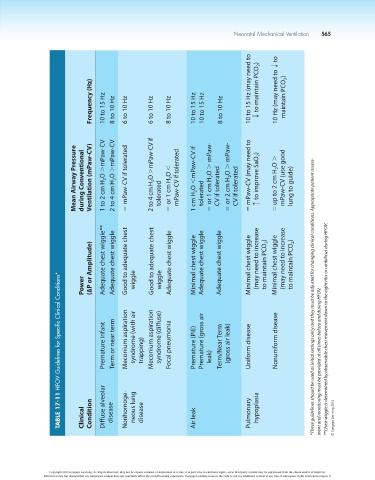
Neonatal Mechanical Ventilation 565
Frequency (Hz) 10 to 15 Hz 8 to 10 Hz 6 to 10 Hz 6 to 10 Hz 8 to 10 Hz 10 to 15 Hz 10 to 15 Hz 8 to 10 Hz 10 to 15 Hz (may need to T to maintain PCO 2 ) 10 Hz (may need to T to maintain PCO 2 )
Mean Airway Pressure during Conventional Ventilation (mPaw-CV) 1 to 2 cm H 2 O .mPaw-CV 2 to 4 cm H 2 O .mPaw-CV 5 mPaw-CV if tolerated 2 to 4 cm H 2 O .mPaw-CV if tolerated 5 or 1 cm H 2 O , mPaw-CV if tolerated 1 cm H 2 O ,mPaw-CV if tolerated 5 or 1 cm H 2 O . mPaw- CV if tolerated 5 or 2 cm H 2 O . mPaw- CV if tolerated 5 mPaw-CV (may need to c to improve SaO 2 ) 5 up to 2 cm H 2 O . mPaw-CV (use good lung to guide)
(∆P or Amplitude) Adequate chest wiggle** Adequate chest wiggle Good to adequate chest Good to adequate chest Adequate chest wiggle Minimal chest wiggle Adequate chest wiggle Adequate chest wiggle Minimal chest wiggle (may need to increase to maintain PCO 2 ) Minimal chest wiggle (may need to increase to maintain PCO 2 )
HFOV Guidelines for Specific Clinical Conditions*
Power wiggle wiggle *These guidelines should be used as initial settings onl,y and they must be adjusted for changing clinical conditions. Appropriate patient assess-
Premature infant Term or near term Meconium aspiration syndrome (with air trapping) Meconium aspiration syndrome (diffuse) Focal pneumonia Premature (PIE) Premature (gross air leak) Term/Near Term (gross air leak) Uniform disease Nonuniform disease ment and monitoring must be provided at all times before and during HFOV. **Chest wiggle is determined by observable chest movement down to the eight ribs or umbilicus during HFOV.
TABLE 17-11 Clinical Condition Diffuse alveolar disease Nonhomoge- neous lung disease Air leak Pulmonary hypoplasia © Cengage Learning 2014
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.