Page 709 - Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation
P. 709
Case Studies 675
-
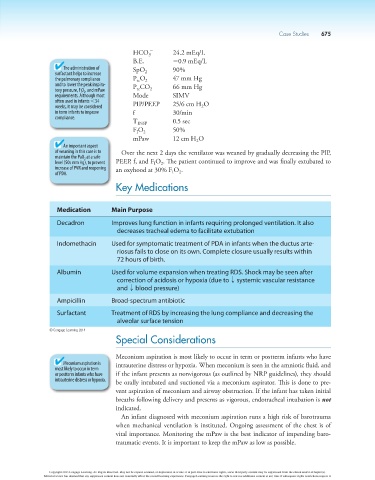
HCO 24.2 mEq/L
3
B.E. 20.9 mEq/L
The administration of SpO 90%
surfactant helps to increase 2
the pulmonary compliance P O 2 47 mm Hg
tc
and to lower the peak inspira- P CO 66 mm Hg
tory pressure, F I O 2 , and mPaw tc 2
requirements. Although most Mode SIMV
often used in infants ,34 PIP/PEEP 25/6 cm H O
weeks, it may be considered 2
in term infants to improve f 30/min
compliance.
T INSP 0.5 sec
F O 2 50%
I
mPaw 12 cm H O
2
An important aspect
of weaning in this case is to Over the next 2 days the ventilator was weaned by gradually decreasing the PIP,
maintain the PaO 2 at a safe
level (50s mm Hg), to prevent PEEP, f, and F O . The patient continued to improve and was finally extubated to
I
2
increase of PVR and reopening an oxyhood at 30% F O .
of PDA. I 2
Key Medications
Medication Main Purpose
Decadron Improves lung function in infants requiring prolonged ventilation. It also
decreases tracheal edema to facilitate extubation
Indomethacin Used for symptomatic treatment of PDA in infants when the ductus arte-
riosus fails to close on its own. Complete closure usually results within
72 hours of birth.
Albumin Used for volume expansion when treating RDS. Shock may be seen after
correction of acidosis or hypoxia (due to T systemic vascular resistance
and T blood pressure)
Ampicillin Broad-spectrum antibiotic
Surfactant Treatment of RDS by increasing the lung compliance and decreasing the
alveolar surface tension
© Cengage Learning 2014
Special Considerations
Meconium aspiration is most likely to occur in term or postterm infants who have
Meconium aspiration is intrauterine distress or hypoxia. When meconium is seen in the amniotic fluid, and
most likely to occur in term
or postterm infants who have if the infant presents as nonvigorous (as outlined by NRP guidelines), they should
intrauterine distress or hypoxia. be orally intubated and suctioned via a meconium aspirator. This is done to pre-
vent aspiration of meconium and airway obstruction. If the infant has taken initial
breaths following delivery and presents as vigorous, endotracheal intubation is not
indicated.
An infant diagnosed with meconium aspiration runs a high risk of barotrauma
when mechanical ventilation is instituted. Ongoing assessment of the chest is of
vital importance. Monitoring the mPaw is the best indicator of impending baro-
traumatic events. It is important to keep the mPaw as low as possible.
Copyright 2013 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.