Page 136 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 136
9/0
0
009
9/2
1-1
p11
qxd
31.
8:2
12
e 1
ara
Apt
M
4 A
g
P
LWB
LWB K34 0-c 05_ p11 1-1 31. qxd 0 9/0 9/2 009 0 0 8:2 4 A M P a a g e 1 12 Apt ara
LWBK340-c05_p111-131.qxd 09/09/2009 08:24 AM Page 112 Aptara
0-c
K34
05_
112 PA R T I I / Physiologic and Pathologic Responses
vascular endothelium located between the vascular lumen and
EXERCISE ANGINA
smooth muscle cells also releases vasoactive substances that ulti-
ACUTE mately regulate vascular tone. These substances are known as
EXERCISE O DEMAND O 2 SUPPLY prostacyclin, nitric oxide, endothelial-derived relaxing factor, and
2
Heart rate coronary vasoconstriction hyperpolarizing factor are potent vasodilators. 6,13,20–23 In addition,
endothelin-1, a potent vasoconstrictor, causes a reduction of Na -/
Afterload blood flow redistribution K -ATPase activity. ATPases are impaired by anoxia and produce
superoxides and free radicals. Thus, decreased oxygen leads to a pro-
n
o o o o o ro ro ro ro ro ro ro ro ro ro r
cor nary
n
o
n
n
n
n
Pre-load stenosis duction of superoxides and hydrogen peroxide, which are highly
n
n
o
o
o
o
o
s
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
diffusible and induce cell damage. Early or chronic atherosclerosis
Contractility ischemic and factors such as dyslipidemia, hypertension, diabetes mellitus,
zone
cigarette smoking, menopause, hyperhomocystinemia, and muta-
tions in nitric oxide synthetase, may inhibit mediator effects and
DEMAND SUPPLY
impair arterial endothelial function, causing increased permeability
of blood lipids and monocytes. 6,17,21,22,24 Further discussion of ath-
O deficit angina erosclerosis is mentioned below.
2
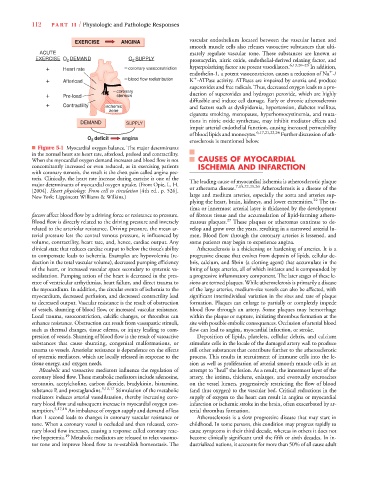
■ Figure 5-1 Myocardial oxygen balance. The major determinants
in the normal heart are heart rate, afterload, preload and contractility.
When the myocardial oxygen demand increases and blood flow is not CAUSES OF MYOCARDIAL
concomitantly increased or even reduced, as in exercising patients ISCHEMIA AND INFARCTION
with coronary stenosis, the result is the chest pain called angina pec-
toris. Clinically, the heart rate increase during exercise is one of the The leading cause of myocardial ischemia is atherosclerotic plaque
major determinants of myocardial oxygen uptake. (From Opie, L. H. 7,15,22,25,26
[2004]. Heart physiology: From cell to circulation [4th ed., p. 526]. or atheroma disease. Atherosclerosis is a disease of the
New York: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.) large and medium arteries, especially the aorta and arteries sup-
22
plying the heart, brain, kidneys, and lower extremities. The in-
tima or innermost arterial layer is thickened by the development
factors affect blood flow by a driving force or resistance to pressure. of fibrous tissue and the accumulation of lipid-forming athero-
Blood flow is directly related to the driving pressure and inversely matous plaques. 27 These plaques or atheromas continue to de-
related to the arteriolar resistance. Driving pressure, the mean ar- velop and grow over the years, resulting in a narrowed arterial lu-
terial pressure less the central venous pressure, is influenced by men. Blood flow through the coronary arteries is lessened, and
volume, contractility, heart rate, and, hence, cardiac output. Any some patients may begin to experience angina.
clinical state that reduces cardiac output to below the tissue’s ability Atherosclerosis is a thickening or hardening of arteries. It is a
to compensate leads to ischemia. Examples are hypovolemia (re- progressive disease that evolves from deposits of lipids, cellular de-
duction in the total vascular volume), decreased pumping efficiency bris, calcium, and fibrin (a clotting agent) that accumulate in the
of the heart, or increased vascular space secondary to systemic va- lining of large arteries, all of which initiates and is compounded by
sodilatation. Pumping action of the heart is decreased in the pres- a progressive inflammatory component. The later stages of these le-
ence of ventricular arrhythmias, heart failure, and direct trauma to sions are termed plaques. While atherosclerosis is primarily a disease
the myocardium. In addition, the circular events of ischemia to the of the large arteries, medium-size vessels can also be affected, with
myocardium, decreased perfusion, and decreased contractility lead significant interindividual variation in the sites and rate of plaque
to decreased output. Vascular resistance is the result of obstruction formation. Plaques can enlarge to partially or completely impede
of vessels, shunting of blood flow, or increased vascular resistance. blood flow through an artery. Some plaques may hemorrhage
Local trauma, vasoconstriction, calcific changes, or thrombus can within the plaque or rupture, initiating thrombus formation at the
enhance resistance. Obstruction can result from vasospastic stimuli, site with possible embolic consequences. Occlusion of arterial blood
such as thermal changes, tissue edema, or injury leading to com- flow can lead to angina, myocardial infarction, or stroke.
pression of vessels. Shunting of blood flow is the result of vasoactive Deposition of lipids, platelets, cellular debris, and calcium
substances that cause shunting, congenital malformations, or stimulate cells in the locale of the damaged artery wall to produce
trauma to vessels. Arteriolar resistance is dependence on the effects still other substances that contribute further to the atherosclerotic
of systemic mediators, which are locally released in response to the process. This results in recruitment of immune cells into the le-
tissue energy, and oxygen needs. sion as well as proliferation of arterial smooth muscle cells in an
Metabolic and vasoactive mediators influence the regulation of attempt to “heal” the lesion. As a result, the innermost layer of the
coronary blood flow. These metabolic mediators include adenosine, artery, the intima, thickens, enlarges, and eventually encroaches
serotonin, acetylcholine, carbon dioxide, bradykinin, histamine, on the vessel lumen, progressively restricting the flow of blood
substance P, and prostaglandins. 5,13,17 Stimulation of the metabolic (and thus oxygen) to the vascular bed. Critical reductions in the
mediators induces arterial vasodilatation, thereby increasing coro- supply of oxygen to the heart can result in angina or myocardial
nary blood flow and subsequent increase in myocardial oxygen con- infarction or ischemic stroke in the brain, often exacerbated by ar-
sumption. 5,17,18 An imbalance of oxygen supply and demand of less terial thrombus formation.
than 1 second leads to changes in coronary vascular resistance or Atherosclerosis is a slow progressive disease that may start in
tone. When a coronary vessel is occluded and then released, coro- childhood. In some persons, this condition may progress rapidly to
nary blood flow increases, causing a response called coronary reac- cause symptoms in their third decade, whereas in others it does not
19
tive hyperemia. Metabolic mediators are released to relax vasomo- become clinically significant until the fifth or sixth decades. In in-
tor tone and improve blood flow to re-establish homeostasis. The dustrialized nations, it accounts for more than 50% of all cause adult