Page 157 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 157
33
33
e 1
P
g
8:2
009
P
5 A
M
Apt
qxd
0
9/2
9/0
p13
ara
2-1
52.
52.
K34
0-c
06_
K34
L L LWB K34 0-c 06_ p13 2-1 52. qxd 0 9/0 9/2 009 0 0 8:2 5 A M P a a g e 1 33 Apt ara
LWB
LWBK340-c06_06_p132-152.qxd 09/09/2009 08:25 AM Page 133 Aptara
C HAPTER 6 / Hematopoiesis, Coagulation, and Bleeding 133
Neutr rophils
CFU–GM
T cell
Mono ocytes
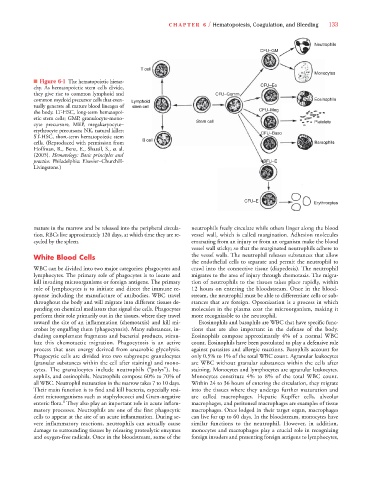
■ Figure 6-1 The hematopoietic hierar-
CFU–Eo
chy. As hematopoietic stem cells divide,
they give rise to common lymphoid and CFU–Gemm
common myeloid precursor cells that even- Lymphoid Eosin ophils
tually generate all mature blood lineages of stem cell
the body. LT-HSC, long-term hematopoi- CFU–Meg
etic stem cells; GMP, granulocyte-mono- Stem cell Platel ets
P
P
cyte precursors; MEP, megakaryocyte–
erythrocyte precursors; NK, natural killer; CFU–Baso
ST-HSC, short-term hematopoietic stem B cell l
cells. (Reproduced with permission from Barso ophils
Hoffman, R., Benz, E., Shattil, S., et al.
(2005). Hematology: Basic principles and
practice. Philadelphia: Elsevier–Churchill- BFU–E
Livingstone.)
CFU–E
Erythr rocytes
mature in the marrow and be released into the peripheral circula- neutrophils freely circulate while others linger along the blood
tion. RBCs live approximately 120 days, at which time they are re- vessel wall, which is called margination. Adhesion molecules
cycled by the spleen. emanating from an injury or from an organism make the blood
vessel wall sticky; so that the marginated neutrophils adhere to
White Blood Cells the vessel walls. The neutrophil releases substances that allow
the endothelial cells to separate and permit the neutrophil to
WBC can be divided into two major categories: phagocytes and crawl into the connective tissue (diapedesis). The neutrophil
lymphocytes. The primary role of phagocytes is to locate and migrates to the area of injury through chemotaxis. The migra-
kill invading microorganisms or foreign antigens. The primary tion of neutrophils to the tissues takes place rapidly, within
role of lymphocytes is to initiate and direct the immune re- 12 hours on entering the bloodstream. Once in the blood-
sponse including the manufacture of antibodies. WBC travel stream, the neutrophil must be able to differentiate cells or sub-
throughout the body and will migrate into different tissues de- stances that are foreign. Opsonization is a process in which
pending on chemical mediators that signal the cells. Phagocytes molecules in theplasma coat the microorganism, making it
perform their role primarily out in the tissues, where they travel more recognizable to the neutrophil.
toward the site of an inflammation (chemotaxis) and kill mi- Esosinophils and basophils are WBC that have specific func-
crobes by engulfing them (phagocytosis). Many substances, in- tions that are also important in the defense of the body.
cluding complement fragments and bacterial products, stimu- Eosinophils compose approximately 4% of a normal WBC
late this chemotactic migration. Phagocytosis is an active count. Eosinophils have been postulated to play a defensive role
process that uses energy derived from anaerobic glycolysis. against parasites and allergic reactions. Basophils account for
Phagocytic cells are divided into two subgroups: granulocytes only 0.5% to 1% of the total WBC count. Agranular leukocytes
(granular substances within the cell after staining) and mono- are WBC without granular substances within the cells after
cytes. The granulocytes include neutrophils (“polys”), ba- staining. Monocytes and lymphocytes are agranular leukocytes.
sophils, and eosinophils. Neutrophils compose 60% to 70% of Monocytes constitute 4% to 8% of the total WBC count.
all WBC. Neutrophil maturation in the marrow takes 7 to 10 days. Within 24 to 36 hours of entering the circulation, they migrate
Their main function is to find and kill bacteria, especially resi- into the tissues where they undergo further maturation and
dent microorganisms such as staphylococci and Gram-negative are called macrophages. Hepatic Kupffer cells, alveolar
1
enteric flora. They also play an important role in acute inflam- macrophages, and peritoneal macrophages are examples of tissue
matory processes. Neutrophils are one of the first phagocytic macrophages. Once lodged in their target organ, macrophages
cells to appear at the site of an acute inflammation. During se- can live for up to 60 days. In the bloodstream, monocytes have
vere inflammatory reactions, neutrophils can actually cause similar functions to the neutrophil. However, in addition,
damage to surrounding tissues by releasing proteolytic enzymes monocytes and macrophages play a crucial role in recognizing
and oxygen-free radicals. Once in the bloodstream, some of the foreign invaders and presenting foreign antigens to lymphocytes,