Page 220 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 220
LWBK340-c08_p177-203.qxd 6/29/09 10:16 PM Page 196 Aptara Inc.
196 PA R T II / Physiologic and Pathologic Responses
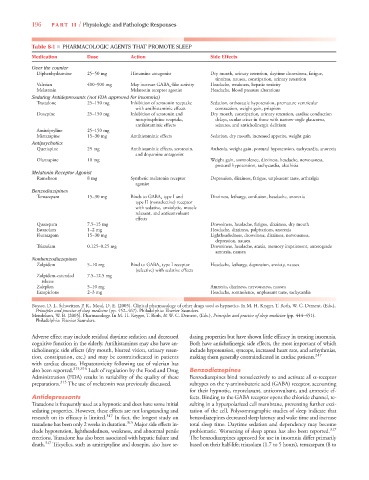
Table 8-1 ■ PHARMACOLOGIC AGENTS THAT PROMOTE SLEEP
Medication Dose Action Side Effects
Over the counter
Diphenhydramine 25–50 mg Histamine antagonist Dry mouth, urinary retention, daytime drowsiness, fatigue,
tinnitus, nausea, constipation, urinary retention
Valerian 400–900 mg May increase GABA a -like activity Headache, weakness, hepatic toxicity
Melatonin Melatonin receptor agonist Headache, blood pressure alterations
Sedating Antidepressants (not FDA approved for insomnia)
Trazadone 25–150 mg Inhibition of serotonin reuptake Sedation, orthostatic hypotension, premature ventricular
with antihistaminic effects contraction, weight gain, priapism
Doxepine 25–150 mg Inhibition of serotonin and Dry mouth, constipation, urinary retention, cardiac conduction
norepinephrine reuptake, delays, ocular crises in those with narrow-angle glaucoma,
antihistaminic effects seizures, and anticholinergic delirium
Amitriptyline 25–150 mg
Mirtazapine 15–30 mg Antihistaminic effects Sedation, dry mouth, increased appetite, weight gain
Antipsychotics
Quetiapine 25 mg Antihistaminic effects, serotonin, Asthenia, weight gain, postural hypotension, tachycardia, anorexia
and dopamine antagonist
Olanzapine 10 mg Weight gain, somnolence, dizziness, headache, nervousness,
postural hypotension, tachycardia, akathisia
Melatonin Receptor Agonist
Ramelteon 8 mg Synthetic melatonin receptor Depression, dizziness, fatigue, unpleasant taste, arthralgia
agonist
Benzodiazipines
Temazepam 15–30 mg Binds to GABA a type I and Dizziness, lethargy, confusion, headache, anorexia
type II (nonselective) receptor
with sedative, anxiolytic, muscle
relaxant, and anticonvulsant
effects
Quazepam 7.5–15 mg Drowsiness, headache, fatigue, dizziness, dry mouth
Estazolam 1–2 mg Headache, dizziness, palpitations, anorexia
Flurazapam 15–30 mg Lightheadedness, drowsiness, dizziness, nervousness,
depression, nausea
Triazolam 0.125–0.25 mg Drowsiness, headache, ataxia, memory impairment, anterograde
amnesia, nausea
Nonbenzodiazepines
Zolpidem 5–10 mg Bind to GABA a type I receptor Headache, lethargy, depression, anxiety, nausea
(selective) with sedative effects
Zolpidem-extended 7.5–12.5 mg
release
Zaleplon 5–10 mg Amnesia, dizziness, nervousness, nausea
Eszopiclone 2–3 mg Headache, somnolence, unpleasant taste, tachycardia
Buysse, D. J., Schweitzer, P. K., Moul, D. E. (2005). Clinical pharmacology of other drugs used as hypnotics. In M. H. Kryger, T. Roth, W. C. Dement, (Eds.),
Principles and practice of sleep medicine (pp. 452–467). Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders.
Mendelson, W. B. (2005). Pharmacology. In M. H. Kryger, T. Roth, & W. C. Dement, (Eds.), Principles and practice of sleep medicine (pp. 444–451).
Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders.
Adverse effect may include residual daytime sedation and decreased dating properties but have shown little efficacy in treating insomnia.
cognitive function in the elderly. Antihistamines may also have an- Both have anticholinergic side effects, the most important of which
ticholinergic side effects (dry mouth, blurred vision, urinary reten- include hypotension, syncope, increased heart rate, and arrhythmias,
tion, constipation, etc.) and may be contraindicated in patients making them generally contraindicated in cardiac patients. 317
with cardiac disease. Hepatotoxicity following use of valerian has
also been reported. 315,316 Lack of regulation by the Food and Drug Benzodiazepines
Administration (FDA) results in variability of the quality of these Benzodiazepines bind nonselectively to and activate all -receptor
preparations. 315 The use of melatonin was previously discussed. subtypes on the -aminobuteric acid (GABA) receptor, accounting
for their hypnotic, myorelaxant, anticonvulsant, and amnestic ef-
Antidepressants fects. Binding to the GABA receptor opens the chloride channel, re-
Trazadone is frequently used as a hypnotic and does have some initial sulting in a hyperpolarized cell membrane, preventing further exci-
sedating properties. However, these effects are not longstanding and tation of the cell. Polysomnographic studies of sleep indicate that
research on its efficacy is limited. 317 In fact, the longest study on benzodiazepines decreased sleep latency and wake time and increase
trazadone has been only 2 weeks in duration. 315 Major side effects in- total sleep time. Daytime sedation and dependency may become
clude hypotension, lightheadedness, weakness, and abnormal penile problematic. Worsening of sleep apnea has also been reported. 317
erections. Trazadone has also been associated with hepatic failure and The benzodiazepines approved for use in insomnia differ primarily
death. 317 Tricyclics, such as amitriptyline and doxepin, also have se- based on their half-life; triazolam (1.7 to 5 hours), temazepam (8 to