Page 520 - Cardiac Nursing
P. 520
9/0
0
9/2
8:2
009
0-5
p46
10.
qxd
10.
96
e 4
96
ara
Apt
M
8 A
P
g
P
LWBK340-c21_21_p460-510.qxd 09/09/2009 08:28 AM Page 496 Aptara
L L LWB
LWB K34 0-c 21_ p46 0-5 10. qxd 0 9/0 9/2 009 0 0 8:2 8 A M P a a g e 4 96 Apt ara
K34
21_
0-c
K34
496 P A R T III / Assessment of Heart Disease
DISPLAY 21-8 Integrated Approach to Fluid functional indices were not used as part of an integrated plan of
Resuscitation care. 479
Research is now being conducted to evaluate the use of func-
1. Is there an indication of end-organ hypoperfusion? tional indices or less invasive CO monitoring as part of an inte-
2. Measure MAP/functional indicators
3. If functional indicator threshold—give 500 mL bolus grated plan of care. For example, high-risk surgical patients were
over 15 minutes and reassess randomized to receive postoperative fluid resuscitation guided by
4. Repeat boluses every 15 minutes until functional indica- CVP (fluid boluses administered to achieve a sustained increased
tor threshold, then stop in CVP of 2 mm Hg lasting for at least 20 minutes) compared
5. If MAP remains 60 mm Hg after initial fluid bolus— with patients receiving fluids to increase their SV by 10% for
#
start norepinephrine at least 20 minutes and dopexamine if their did not exceed
2
6. If functional indicator threshold and vasopressor 600 mL/min/m . Patients in the goal-directed group had few com-
therapy is still required—evaluate cardiac contractility plications and a shorter length of stay. Although this study used an
(echo) LiDCO monitor, which provides functional indices, because many
7. If contractility is impaired -consider dobutamine
of the patients were extubated early, the functional indices were not
used as part of the protocol to determine if fluid therapy was the
Adapted from Pinsky, M. (2002). Functional hemodynamic monitoring: Applied physi- appropriate intervention. It would be interesting to determine the
ology at the bedside. In J. L. Vincent (Ed.), Intensive care medicine. Annual update
2002 (pp. 537–552). Berlin, Germany: Springer-Verlag. effect of additional tailoring of fluid administration using prospec-
tive functional indices, rather than retrospectively depending on
the SV response.
and UOP 0.5 mL/kg/h. Further research to evaluate protocols Pinsky 255 proposed an algorithm that integrates functional
to achieve these endpoints and the effect of this goal-directed ap- and standard hemodynamic indices to guide resuscitation (Dis-
proach needs to be conducted. play 21-8). Functional and standard hemodynamic indices can
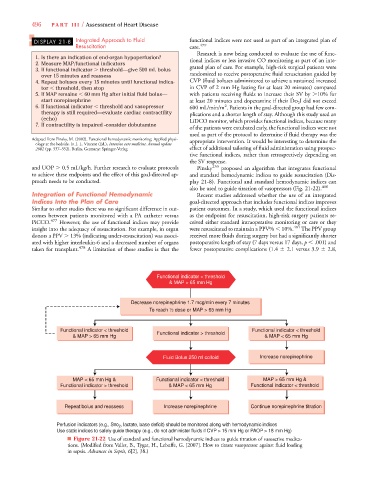
also be used to guide titration of vasopressors (Fig. 21-22). 480
Integration of Functional Hemodynamic Recent studies addressed whether the use of an integrated
Indices Into the Plan of Care goal-directed approach that includes functional indices improves
Similar to other studies there was no significant difference in out- patient outcomes. In a study, which used the functional indices
comes between patients monitored with a PA catheter versus as the endpoint for resuscitation, high-risk surgery patients re-
PiCCO. 477 However, the use of functional indices may provide ceived either standard intraoperative monitoring or care or they
insight into the adequacy of resuscitation. For example, in organ were resuscitated to maintain a PPV% 10%. 481 The PPV group
donors a PPV 13% (indicating under-resuscitation) was associ- received more fluids during surgery but had a significantly shorter
ated with higher interleukin-6 and a decreased number of organs postoperative length of stay (7 days versus 17 days, p .001) and
taken for transplant. 478 A limitation of these studies is that the fewer postoperative complications (1.4 2.1 versus 3.9 2.8,
Functional indicator < threshold
& MAP > 65 mm Hg
se norepinephrine 1.7 mcg/min every 7 minutes
To reach ½ dose or MAP > 65 mm Hg
Functional indicator < threshold Functional indicator > threshold Functional indicator < threshold
& MAP > 65 mm Hg & MAP < 65 mm Hg
Fluid Bolus 250 ml colloid Increase norepinephrine
MAP < 65 mm Hg & Functional indicator < threshold MAP > 65 mm Hg &
Functional indicator > threshold & MAP < 65 mm Hg Functional indicator < threshold
Repeat bolus and reassess Increase norepinephrine Continue norepinephrine titration
, lactate, base deficit) should be monitored along with hemodynamic indices
Perfusion indicators (e.g., Svo 2
Use static indices to safely guide therapy (e.g., do not administer fluids if CVP > 15 mm Hg or PAOP > 18 mm Hg)
■ Figure 21-22 Use of standard and functional hemodynamic indices to guide titration of vasoactive medica-
tions. (Modified from Vallet, B., Tygat, H., Lebuffe, G. [2007]. How to titrate vasopressor against fluid loading
6
6
in sepsis. Advances in Sepsis, 6[2], 38.)