Page 157 - untitled
P. 157
AAAC70 21/5/05 11:00 AM Page 156
70 The ear, and lymphatics and surface anatomy of the head and neck
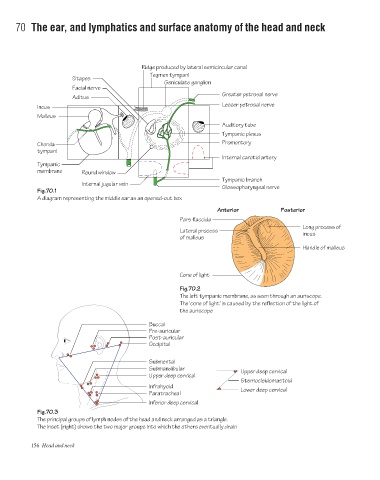
Ridge produced by lateral semicircular canal
Tegmen tympani
Stapes
Geniculate ganglion
Facial nerve
Greater petrosal nerve
Aditus
Incus Lesser petrosal nerve
Malleus
Auditory tube
Tympanic plexus
Chorda Promontory
tympani
Internal carotid artery
Tympanic
membrane Round window
Tympanic branch
Internal jugular vein
Glossopharyngeal nerve
Fig.70.1
A diagram representing the middle ear as an opened-out box
Anterior Posterior
Pars flaccida
Long process of
Lateral process incus
of malleus
Handle of malleus
Cone of light
Fig.70.2
The left tympanic membrane, as seen through an auriscope.
The 'cone of light' is caused by the reflection of the light of
the auriscope
Buccal
Pre-auricular
Post-auricular
Occipital
Submental
Submandibular
Upper deep cervical
Upper deep cervical
Sternocleidomastoid
Infrahyoid
Lower deep cervical
Paratracheal
Inferior deep cervical
Fig.70.3
The principal groups of lymph nodes of the head and neck arranged as a triangle.
The inset (right) shows the two major groups into which the others eventually drain
156 Head and neck