Page 152 - untitled
P. 152
AAAC67 21/5/05 11:01 AM Page 151
Nerves
Arteries
Supratrochear
Supratrochear
Supraorbital
Supraorbital
Auriculotemporal Superficial temporal
Lesser occipital Posterior auricular
Greater occipital
Occipital
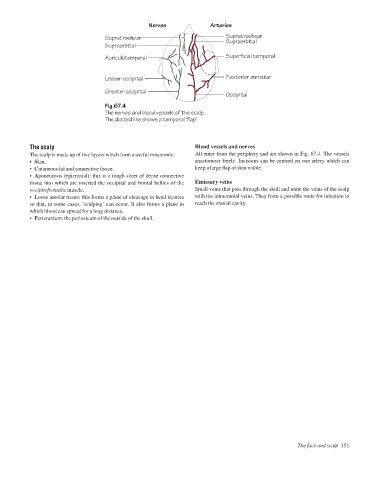
Fig.67.4
The nerves and blood vessels of the scalp.
The dotted line shows a temporal 'flap'
The scalp Blood vessels and nerves
The scalp is made up of five layers which form a useful mnemonic: All enter from the periphery and are shown in Fig. 67.4. The vessels
• Skin. anastomose freely. Incisions can be centred on one artery which can
• Cutaneous fat and connective tissue. keep a large flap of skin viable.
• Aponeurosis (epicranial): this is a tough sheet of dense connective
tissue into which are inserted the occipital and frontal bellies of the Emissary veins
occipitofrontalis muscle. Small veins that pass through the skull and unite the veins of the scalp
• Loose areolar tissue: this forms a plane of cleavage in head injuries with the intracranial veins. They form a possible route for infection to
so that, in some cases, ‘scalping’ can occur. It also forms a plane in reach the cranial cavity.
which blood can spread for a long distance.
• Pericranium: the periosteum of the outside of the skull.
The face and scalp 151