Page 153 - untitled
P. 153
AAAC68 21/5/05 11:01 AM Page 152
68 The cranial cavity
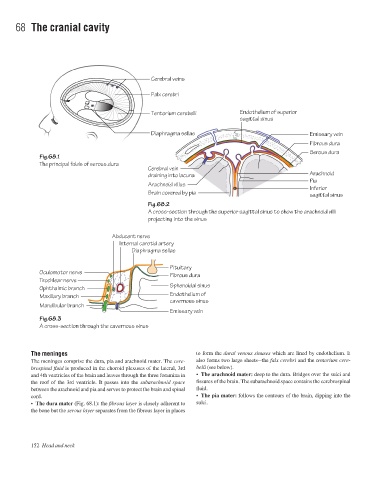
Cerebral veins
Falx cerebri
Tentorium cerebelli Endothelium of superior
sagittal sinus
Diaphragma sellae Emissary vein
Fibrous dura
Serous dura
Fig.68.1
The principal folds of serous dura
Cerebral vein
draining into lacuna Arachnoid
Pia
Arachnoid villus
Inferior
Brain covered by pia sagittal sinus
Fig.68.2
A cross-section through the superior sagittal sinus to show the arachnoid villi
projecting into the sinus
Abducent nerve
Internal carotid artery
Diaphragma sellae
Pituitary
Oculomotor nerve
Fibrous dura
Trochlear nerve
Sphenoidal sinus
Ophthalmic branch
Endothelium of
Maxillary branch
cavernous sinus
Mandibular branch
Emissary vein
Fig.68.3
A cross-section through the cavernous sinus
The meninges to form the dural venous sinuses which are lined by endothelium. It
The meninges comprise the dura, pia and arachnoid mater. The cere- also forms two large sheetsathe falx cerebri and the tentorium cere-
brospinal fluid is produced in the choroid plexuses of the lateral, 3rd belli (see below).
and 4th ventricles of the brain and leaves through the three foramina in • The arachnoid mater: deep to the dura. Bridges over the sulci and
the roof of the 3rd ventricle. It passes into the subarachnoid space fissures of the brain. The subarachnoid space contains the cerebrospinal
between the arachnoid and pia and serves to protect the brain and spinal fluid.
cord. • The pia mater: follows the contours of the brain, dipping into the
• The dura mater (Fig. 68.1): the fibrous layer is closely adherent to sulci.
the bone but the serous layer separates from the fibrous layer in places
152 Head and neck