Page 181 - Color Atlas Of Pathophysiology (S Silbernagl Et Al, Thieme 2000)
P. 181
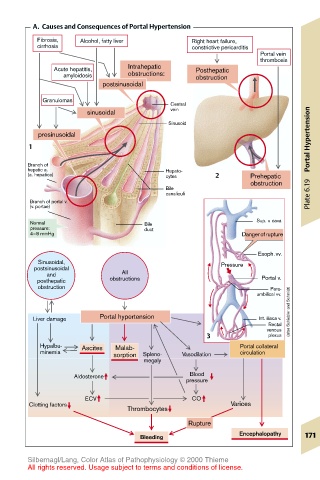
A. Causes and Consequences of Portal Hypertension
Fibrosis, Alcohol, fatty liver Right heart failure,
cirrhosis constrictive pericarditis
Portal vein
thrombosis
Intrahepatic
Acute hepatitis, Posthepatic
amyloidosis obstructions: obstruction
postsinusoidal
Granulomas
Central
sinusoidal vein
Sinusoid
presinusoidal Portal Hypertension
1
Branch of
hepatic a. Hepato-
(a. hepatica) cytes 2 Prehepatic
obstruction
Bile
canaliculi Plate 6.19
Branch of portal v.
(v. portae)
Sup. v. cava
Normal Bile
pressure: duct
4–8 mmHg Danger of rupture
Esoph.vv.
Sinusoidal, Pressure
postsinusoidal
and All
posthepatic obstructions Portal v.
obstruction Para-
umbilical vv.
Liver damage Portal hypertension Int. iliaca v. (after Schiebler and Schmidt)
Rectal
venous
3 plexus
Hypalbu- Ascites Malab- Portal collateral
minemia circulation
sorption Spleno- Vasodilation
megaly
Aldosterone Blood
pressure
ECV CO
Clotting factors Varices
Thrombocytes
Rupture
Encephalopathy
Bleeding 171
Silbernagl/Lang, Color Atlas of Pathophysiology © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.