Page 205 - Color Atlas Of Pathophysiology (S Silbernagl Et Al, Thieme 2000)
P. 205
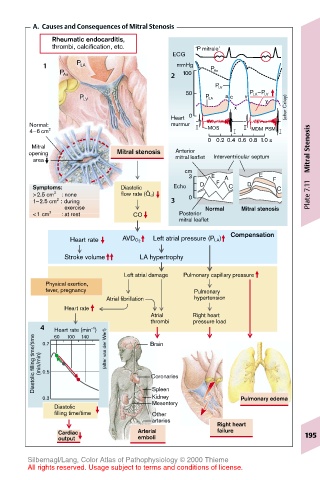
A. Causes and Consequences of Mitral Stenosis
Rheumatic endocarditis,
thrombi, calcification, etc. ‘P mitrale’
ECG
1 P LA mmHg P Ao
2
P Ao 100
P LV
50 P LA –P LV
y
P LV P LA a c v
x (after Criley)
Heart 0
Normal: murmur MOS
4–6 cm 2 MDM PSM
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 s
Mitral Mitral Stenosis
opening Mitral stenosis Anterior Interventricular septum
area mitral leaflet
cm
3 E A E F
Symptoms: Diastolic . Echo D F C D C
>2.5 cm 2 : none flow rate (Q d ) 0 Plate 7.11
2
1–2.5 cm : during 3
exercise Normal Mitral stenosis
2
<1 cm : at rest CO Posterior
mitral leaflet
Compensation
Heart rate AVD O 2 Left atrial pressure (P LA)
Stroke volume LA hypertrophy
Left atrial damage Pulmonary capillary pressure
Physical exertion,
fever, pregnancy Pulmonary
Atrial fibrillation hypertension
Heart rate
Atrial Right heart
thrombi pressure load
4 0.7 Heart rate (min ) Brain
–1
60
Diastolic filling time/time (min/min) 0.5 (after van der Werf) Coronaries
100
140
Kidney
0.3 Spleen Pulmonary edema
Diastolic Mesentery
filling time/time Other
arteries
Right heart
Cardiac Arterial failure 195
output emboli
Silbernagl/Lang, Color Atlas of Pathophysiology © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.