Page 271 - Color Atlas Of Pathophysiology (S Silbernagl Et Al, Thieme 2000)
P. 271
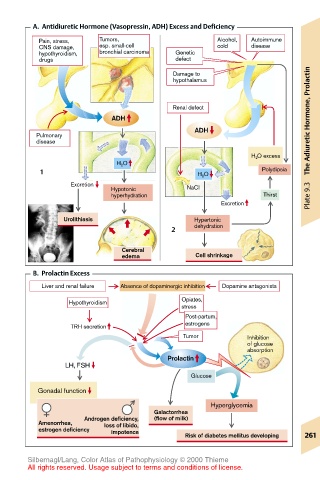
A. Antidiuretic Hormone (Vasopressin, ADH) Excess and Deficiency
Pain, stress, Tumors, Alcohol, Autoimmune
CNS damage, esp. small-cell cold disease
hypothyroidism, bronchial carcinoma Genetic
drugs defect
Damage to
hypothalamus
Renal defect
ADH Adiuretic Hormone, Prolactin
ADH
Pulmonary
disease
H 2 O excess
H 2 O
1 H 2 O Polydipsia The
Excretion
Hypotonic NaCl
hyperhydration Thirst Plate 9.3
Excretion
Urolithiasis Hypertonic
2 dehydration
Cerebral
edema Cell shrinkage
B. Prolactin Excess
Liver and renal failure Absence of dopaminergic inhibition Dopamine antagonists
Opiates,
Hypothyroidism
stress
Post-partum,
estrogens
TRH secretion
Tumor Inhibition
of glucose
absorption
Prolactin
LH, FSH
Glucose
Gonadal function
Hyperglycemia
Galactorrhea
Androgen deficiency, (flow of milk)
Amenorrhea, loss of libido,
estrogen deficiency impotence
Risk of diabetes mellitus developing 261
Silbernagl/Lang, Color Atlas of Pathophysiology © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.